15th Aug 2010, 15:54
permalink Post: 10
TURIN
,
I've read "By the Rivers of Babylon" too..... and there is some fact behind the fiction.
History does not relate if and where the El Al Concordes would have had APUs.
However, history DOES relate, that the two Concordes ordered by Iran Air WOULD have had APUs (which would have made sense in the Middle East).
Now, Iran Air was the very last company to cancel its orders, and by the time they did, Concorde 214 (now G-BOAG) and 216 (now G-BOAF) were already well underway (they ended up flying initially as white tails).
As a result, both 214 and 216 still have the mounting holes and fittings for an APU. Don't ask me where, but experts know where to find them to this day....
I've read "By the Rivers of Babylon" too..... and there is some fact behind the fiction.
History does not relate if and where the El Al Concordes would have had APUs.
However, history DOES relate, that the two Concordes ordered by Iran Air WOULD have had APUs (which would have made sense in the Middle East).
Now, Iran Air was the very last company to cancel its orders, and by the time they did, Concorde 214 (now G-BOAG) and 216 (now G-BOAF) were already well underway (they ended up flying initially as white tails).
As a result, both 214 and 216 still have the mounting holes and fittings for an APU. Don't ask me where, but experts know where to find them to this day....
16th Aug 2010, 12:09
permalink Post: 11
ChristiaanJ
Both A/C 214 (OAG) and 216 (OAF) were Variant 192 A/C (British Unsold A/C). 216 was later converted to a 102 (British Airways) Variant, where 214 more or less stayed as a Variant 192. I'm not disputing what you say about possible APU mountings (I guess it would HAVE to be at the front section of the lower cargo hold somewhere) but I for one have certainly never seen any evidence of them. I'm still trying to imagine where the air inlet and exhausts would have to be arranged, not to mention pneumatic services ducting/hydraulics. Wouldn't it be interesting to find out?
Both A/C 214 (OAG) and 216 (OAF) were Variant 192 A/C (British Unsold A/C). 216 was later converted to a 102 (British Airways) Variant, where 214 more or less stayed as a Variant 192. I'm not disputing what you say about possible APU mountings (I guess it would HAVE to be at the front section of the lower cargo hold somewhere) but I for one have certainly never seen any evidence of them. I'm still trying to imagine where the air inlet and exhausts would have to be arranged, not to mention pneumatic services ducting/hydraulics. Wouldn't it be interesting to find out?

17th Aug 2010, 14:33
permalink Post: 17
M2dude,
Nice set of photos of "The Thing" here :
MEPU at MAE at le Bourget .
This one is at the Air and Space Museum at Le Bourget, near Paris. My guess is that is was a spare, since the manufacturing date is 1973. 'SA flew in January '73 and 'SB in December '73.
IIRC, Delta Golf arrived at Brooklands with the MEPU still in place; I might have a photo.
As to the installation, we're obviously thinking along the same lines....
However, there were already several conduits through tank 11, such as hydraulics for the tail wheel, various electrics, and the 'backbone' fuel manifolds, that ended at the fuel jettison port in the tailcone.
A couple of fairly substantial air ducts would only have displaced a few hundred kgs of fuel at the most, out of the more than 10,000 kgs in tank 11.
And yes, of course, the whole point of the APU would be to have independent ground start and ground airco available, so clearly an APU would have been bigger and heavier than the MEPU (which was only just over 80 lbs), plus the problem of the air intake and bigger exhaust.
I'd have to get the drawings out to see how easy or difficult it would have been to fit one in the available space.
Since the tailcone was BAC, and both 214 and 216 were built at Filton, I wonder if anybody there still remembers?
Nice set of photos of "The Thing" here :
MEPU at MAE at le Bourget .
This one is at the Air and Space Museum at Le Bourget, near Paris. My guess is that is was a spare, since the manufacturing date is 1973. 'SA flew in January '73 and 'SB in December '73.
IIRC, Delta Golf arrived at Brooklands with the MEPU still in place; I might have a photo.
As to the installation, we're obviously thinking along the same lines....
However, there were already several conduits through tank 11, such as hydraulics for the tail wheel, various electrics, and the 'backbone' fuel manifolds, that ended at the fuel jettison port in the tailcone.
A couple of fairly substantial air ducts would only have displaced a few hundred kgs of fuel at the most, out of the more than 10,000 kgs in tank 11.
And yes, of course, the whole point of the APU would be to have independent ground start and ground airco available, so clearly an APU would have been bigger and heavier than the MEPU (which was only just over 80 lbs), plus the problem of the air intake and bigger exhaust.
I'd have to get the drawings out to see how easy or difficult it would have been to fit one in the available space.
Since the tailcone was BAC, and both 214 and 216 were built at Filton, I wonder if anybody there still remembers?
20th Aug 2010, 23:21
permalink Post: 39
Quote:
|
ChristiaanJ
As far as the APU ducting issue goes (hee, hee, not often we disagree Christiaan  ) we are just going to have to agree to disagee about this, although I accept that two 4" diameter pipes (PLUS THERMAL INSULATION) might have done it, BUT I still stand by the other points.
) we are just going to have to agree to disagee about this, although I accept that two 4" diameter pipes (PLUS THERMAL INSULATION) might have done it, BUT I still stand by the other points.

|
So I happily agree to disagree on the rest... between the two of us, each looking at our own clues, and with the help of anybody else who has more info, we might still find the answer!
One thought I had... with an APU in the forward baggage hold, you'd also have to take the air intake and exhaust through the pressure hull, and provide sound and thermal insulation for the entire APU itself.
From a design point of view, I'd have gone for the same location of the earlier pseudo-APU (the MEPU), and then solved the remaining problems from that starting point.
24th Aug 2010, 12:02
permalink Post: 90
MEMORIES
Like so many in the Concorde family, I have millions, I'd like to share a couple here. I remember at Fairford in mid 1974, a CAA test pilot (I honestly forget the gentleman's name) was taking the British pre-production A/C 101 (G-AXDN) for a special test flight. The reason that this flight was so special was that for the first time, the CAA were going to do an acceptance flight trial of the brand new digital air intake system. This revolutionary system had been retro fitted to 101 barely a year earlier, and being a brand new (and totally unique, in electronics terms) system had been plagued with teething troubles. It was quite reasonable for any airworthiness authority to have serious misgivings about any system that was going to wave great big metal lumps around in front of the engine compressor face, and that if only a few degrees out from the commanded position out could cause the engine to 'backfire' etc.
So anyway, 101 took off and disappeared into the very blue sky and we waited, and waited, AND WAITED. (I'd only left the RAF and joined the project a few months previously, and did not want my new association with this amazing aircraft to end). I was biting my nails, drinking coffee, losing my hair... (without the help of M2V ). Anyway after about 2 1/2 hours the aircraft returned to Fairford, and everybody crowds around the crew for the debrief. A very stern faced CAA pilot looked at us all, broke into a grin and said "as far as I'm concerned gentlemen, you've got yourselves an airliner". At that point the room was a study of total happiness, blessed relief, and a need to go to the loo..... But from my point of view, I will remember those words forever.
). Anyway after about 2 1/2 hours the aircraft returned to Fairford, and everybody crowds around the crew for the debrief. A very stern faced CAA pilot looked at us all, broke into a grin and said "as far as I'm concerned gentlemen, you've got yourselves an airliner". At that point the room was a study of total happiness, blessed relief, and a need to go to the loo..... But from my point of view, I will remember those words forever.
101, which now resides at the Imperial War Museum Duxford was the fastest Concorde ever. She achieved Mach 2.23, which was an incredible irony, as Concorde can trace a large part of it's developement history back to the BAC 223, proposed SST.
As far as flying memories go, I just don't know where to start; My first ever Concorde flight was in November 1976, out of Fairford on a pre-delivery test flight on G-BOAD. (Now sadly bobbing up and down on the Hudson, next to the USS Intrepid). I was staggered how fast and high we flew (Mach 2.08, FL580). Most of my flying up to that date had been in C-130's in the RAF, at around 340 KTS and FL300; Concorde also being infinately quiter in flight than the good old Herc'. I remember a BA QA guy showing me how I could touch the skin of the aircraft at Mach 2 (You reached behind a door busstle flap, moved your hand through some insulation until you felt bare metal). OUCH!! it was hot, very hot.
But I think one of my most memorable flight memories was aboard G-BOAG, (now residing in the Boeing Museum of Flight in Seattle) returning from BKK, having stopped off to refuel in BAH. We were forced to fly subsonic over Saudi, and got caught in this amazing electrical storm, There was St Elmo's fire cracking and bubbling all over the visor panels, but just as incredible was the long blue electrical discharge coming off of the nose probe; it seemed to extend about 50' in front of the aircraft. The crime was, none of us on the F/D had a camera. Every time I bump into the captain on that day (are you reading this Ian?), we go back to remonissing about that incredible flight. Also, later on the same sector, after we had decelerated to subsonic cruise again, this time flying up the Adriatic, we had another fascinating sight: It was getting quite dark now, and here we were, travelling at Mach 0.95 at FL290, when above us was all this Mach 0.8 ish traffic at around FL330-350. All we could see were all these navigation and ant-coll' lights above us, seemingly travelling backwards. It was quite a sight. On the original BAH-BKK sector a week earlier, we flew through some of the coldest air I'd ever seen; The air was at ISA -25, and at Mach 2 our TAT was only about 85 deg's C. (You could feel the difference too; the cabin windows felt only warm-ish to the touch). The upside also of all this was that your fuel burn was much lower than usual. (The only downside of course is that your TAS is a little lower). Rolls Royce did some analysis on the flight, and were amazed at how well the propulsion systems coped with some of the temperature sheers that we encountered, sometimes 4 to 5 deg's/second. They said that the prototype AFCS had been defeated by rises of only 0.25 deg's/second ).
Not meaning to go off onto a (yet another) tangent; Negative temperature shears, very common at lower lattidudes, always plagued the development aircraft; you would suddenly accelerate, and in the case of a severe shear, would accelerate and accelerate!! (Your Mach number, quite naturaly, suddenly increased with the falling temperature of course, but because of the powerplant suddenly hitting an area of hyper-efficiencey, the A/C would physically accelerate rapidly, way beyond Mmo). Many modifications were tried to mitigate the effects of severe shears, in the end a clever change to the intake control unit software fixed it. (Thanks to this change the production series A/C would not be capable of level flight Mach numbers of any more than Mach 2.13, remembering that Mmo was set at 2.04).
There was one lovely story, involving the Shah of Iran, having one of MANY flights in a developmment aircraft. The aircraft encounterd quite a hefty series of temperature shears that plagued havoc with some Iranian F4's that were attempting to close on the Concorde, to act as an escort for the Shah. (or so the strory goes). I'm still trying to picture these F4's, on full afterburner trying to get close to a Concorde cruising away on dry power). It is said that the F4's were having such difficulties, due to their relatively crude powerplant, coping with the temperature changes, that the Concorde was ordered to slow down, 'so the escorting F4's could catch up'!! True or not, it is part of Concorde folklore.
Dude
Like so many in the Concorde family, I have millions, I'd like to share a couple here. I remember at Fairford in mid 1974, a CAA test pilot (I honestly forget the gentleman's name) was taking the British pre-production A/C 101 (G-AXDN) for a special test flight. The reason that this flight was so special was that for the first time, the CAA were going to do an acceptance flight trial of the brand new digital air intake system. This revolutionary system had been retro fitted to 101 barely a year earlier, and being a brand new (and totally unique, in electronics terms) system had been plagued with teething troubles. It was quite reasonable for any airworthiness authority to have serious misgivings about any system that was going to wave great big metal lumps around in front of the engine compressor face, and that if only a few degrees out from the commanded position out could cause the engine to 'backfire' etc.
So anyway, 101 took off and disappeared into the very blue sky and we waited, and waited, AND WAITED. (I'd only left the RAF and joined the project a few months previously, and did not want my new association with this amazing aircraft to end). I was biting my nails, drinking coffee, losing my hair... (without the help of M2V
 ). Anyway after about 2 1/2 hours the aircraft returned to Fairford, and everybody crowds around the crew for the debrief. A very stern faced CAA pilot looked at us all, broke into a grin and said "as far as I'm concerned gentlemen, you've got yourselves an airliner". At that point the room was a study of total happiness, blessed relief, and a need to go to the loo..... But from my point of view, I will remember those words forever.
). Anyway after about 2 1/2 hours the aircraft returned to Fairford, and everybody crowds around the crew for the debrief. A very stern faced CAA pilot looked at us all, broke into a grin and said "as far as I'm concerned gentlemen, you've got yourselves an airliner". At that point the room was a study of total happiness, blessed relief, and a need to go to the loo..... But from my point of view, I will remember those words forever.
101, which now resides at the Imperial War Museum Duxford was the fastest Concorde ever. She achieved Mach 2.23, which was an incredible irony, as Concorde can trace a large part of it's developement history back to the BAC 223, proposed SST.
As far as flying memories go, I just don't know where to start; My first ever Concorde flight was in November 1976, out of Fairford on a pre-delivery test flight on G-BOAD. (Now sadly bobbing up and down on the Hudson, next to the USS Intrepid). I was staggered how fast and high we flew (Mach 2.08, FL580). Most of my flying up to that date had been in C-130's in the RAF, at around 340 KTS and FL300; Concorde also being infinately quiter in flight than the good old Herc'. I remember a BA QA guy showing me how I could touch the skin of the aircraft at Mach 2 (You reached behind a door busstle flap, moved your hand through some insulation until you felt bare metal). OUCH!! it was hot, very hot.
But I think one of my most memorable flight memories was aboard G-BOAG, (now residing in the Boeing Museum of Flight in Seattle) returning from BKK, having stopped off to refuel in BAH. We were forced to fly subsonic over Saudi, and got caught in this amazing electrical storm, There was St Elmo's fire cracking and bubbling all over the visor panels, but just as incredible was the long blue electrical discharge coming off of the nose probe; it seemed to extend about 50' in front of the aircraft. The crime was, none of us on the F/D had a camera. Every time I bump into the captain on that day (are you reading this Ian?), we go back to remonissing about that incredible flight. Also, later on the same sector, after we had decelerated to subsonic cruise again, this time flying up the Adriatic, we had another fascinating sight: It was getting quite dark now, and here we were, travelling at Mach 0.95 at FL290, when above us was all this Mach 0.8 ish traffic at around FL330-350. All we could see were all these navigation and ant-coll' lights above us, seemingly travelling backwards. It was quite a sight. On the original BAH-BKK sector a week earlier, we flew through some of the coldest air I'd ever seen; The air was at ISA -25, and at Mach 2 our TAT was only about 85 deg's C. (You could feel the difference too; the cabin windows felt only warm-ish to the touch). The upside also of all this was that your fuel burn was much lower than usual. (The only downside of course is that your TAS is a little lower). Rolls Royce did some analysis on the flight, and were amazed at how well the propulsion systems coped with some of the temperature sheers that we encountered, sometimes 4 to 5 deg's/second. They said that the prototype AFCS had been defeated by rises of only 0.25 deg's/second ).
Not meaning to go off onto a (yet another) tangent; Negative temperature shears, very common at lower lattidudes, always plagued the development aircraft; you would suddenly accelerate, and in the case of a severe shear, would accelerate and accelerate!! (Your Mach number, quite naturaly, suddenly increased with the falling temperature of course, but because of the powerplant suddenly hitting an area of hyper-efficiencey, the A/C would physically accelerate rapidly, way beyond Mmo). Many modifications were tried to mitigate the effects of severe shears, in the end a clever change to the intake control unit software fixed it. (Thanks to this change the production series A/C would not be capable of level flight Mach numbers of any more than Mach 2.13, remembering that Mmo was set at 2.04).
There was one lovely story, involving the Shah of Iran, having one of MANY flights in a developmment aircraft. The aircraft encounterd quite a hefty series of temperature shears that plagued havoc with some Iranian F4's that were attempting to close on the Concorde, to act as an escort for the Shah. (or so the strory goes). I'm still trying to picture these F4's, on full afterburner trying to get close to a Concorde cruising away on dry power). It is said that the F4's were having such difficulties, due to their relatively crude powerplant, coping with the temperature changes, that the Concorde was ordered to slow down, 'so the escorting F4's could catch up'!! True or not, it is part of Concorde folklore.
Dude

Last edited by M2dude; 24th Aug 2010 at 15:31 . Reason: spelling (again) :-(
2nd Sep 2010, 00:25
permalink Post: 185
As a BA apprentice in the early eighties I spent 12 months in the old 'wing hangar' (TBB) cutting my teeth, as it were, on the future of aviation. (The newly introduced B757 was also housed there so I was partly right). I was still growing-9 stone wet through and I had to run around in the rain to get wet-so if there was work to be done in the "Bent Nail's" fuel tanks then I was volunteered. Pouring tins and tins of Thiokols best sealant along leaking joints was a favoured pastime, so it begs the question were the leaks ever plugged?
I have a load of photos of G-BOAG just before it was reintroduced (rebuilt?) into service after being a Christmas tree for years. I think it was taken out of service after the wrong hydraulic fluid was uplifted but I may be wrong there. Never seen so many robbery labels before or since. If I ever get my scanner I'll post 'em up one day.
Fascinating thread gents, keep it going.
I have a load of photos of G-BOAG just before it was reintroduced (rebuilt?) into service after being a Christmas tree for years. I think it was taken out of service after the wrong hydraulic fluid was uplifted but I may be wrong there. Never seen so many robbery labels before or since. If I ever get my scanner I'll post 'em up one day.
Fascinating thread gents, keep it going.

Last edited by TURIN; 2nd Sep 2010 at 10:10 . Reason: Apostrophe police out to get me.
2nd Sep 2010, 23:55
permalink Post: 192
Hi canuck slf, Your incident was not the hydraulic contamination one, I'll describe that one in a minute or so below.
As far as your adventure goes, in the early days of Concorde operation there was an on-going issue of hydraulic seal failures. This led to the sort of thing that you described, where a major seal failure would occur, resulting in the loss of a main system. The standby Yellow system would be switched in to replace the failed one, and depending on the nature of the initial failure, could leak out of the same failed seal. (There were a couple of 'common areas', they were the intake spill door jack, and the Powered Flying Control Units; failures here could result in a double system fail). Your incident was almost certainly due to one of these cases. In the early 1990's the original Neoprene hydraulic seals were replaced with a new Viton GLT seal; this material had far superior age shrinking characteristics to Neoprene, and more or less cured the problem overnight. Eventually all the seals in each aircraft were replaced, and apart from a very few isolated cases, dual system losses were eliminated forever. Air France suffered a similar proportion of failures, however as their flying hours were a fraction of BA's, the effects were not as immediately apparent.
As far as far as the hydraulic contamination story goes, this happened in 1980 but involved one aircraft only, G-BOAG, but in it's original registration of G-BFKW. (having previously been on loan from British Aerospace, where it flew originally as a 'white tail' under this registration). The fragile nature of Concorde hydraulic fluid was not fully understood at this time, and as you say, a hydraulic drum dispenser had inadvertently been left exposed to the atmosphere, and had subsequently suffered water contamination, and this contaminated fluid had found it's way into G-BOAG. Now this hydraulic fluid, CHEVRON M2V has only two vices: One is that is extremely expensive, and the second is that it is highly susceptible to water contamination, EXTEMELY SO. If my memory serves me correctly, the maximum allowable level of water in the fluid is about 8ppm. (parts per million) and the fluid that was analysed after G-BOAG's problems was at about 30 ppm. The water deposits in the fluid gave the equivalent effect of 'rusting up' of critical hydraulic components. I was investigating an air intake control defect the previous day to the incident, but like everybody else had no idea that the real issue here was one of major systems contamination. We were all convinced that we had nailed the problem, only to find that the aircraft turned back on it's subsequent LHR-JFK sector with more serious problems, not only affecting the air intakes, but the artificial feel system also. It was now that we realised that there had to be a hydraulics problem here, and after fluid analysis, the awful truth was discovered. After this event, and the fragilities of M2V fluid were better understood, a strict regime of housekeeping was put in place in terms of fluid storage, and no such incidents with BA ever occurring again. The aircraft itself did not fly again for nine months, all components that were affected were removed from the aircraft and completely stripped and overhauled. Also all of the system hydraulic lines had to be completely purged, until there were no further traces of any contamination. After the aircraft was finally rectified, she successfully again returned to service with her new 'BA' registration of G-BOAG. However the following year, during a C Check, it was decided that due to spares shortages, and the closure of the LHR-BAH-SIN route, there just was not being enough work for seven aircraft, and therefore G-BOAG would be withdrawn from service. (In terms of spares, BA at the time for instance only had six sets of aircraft galleys, as aircraft went in for C checks the galley was 'robbed' to service the aircraft coming out of it's own C check). The aircraft was parked in a remote hangar, and was only visited when a component had to be 'robbed' for another Concorde, and the aircraft soon fell into disrepair, was filthy externally and became a really sad sight. Many people (not myself I might add) were adamant that G-BOAG would never fly again. However, in 1984 things had really started to improve for Concorde, with the charter business increasing and the LHR-JFK route in particular becoming a staggering success. It was decided that OAG would be returned to an airworthy condition. In 1985, with a fresh new interior, and with the new BA colour scheme, she was finally returned to service; and remained as one of the mainstays of the fleet right up to the end of Concorde services in October 2003. She now resides at the Boeing Museum of Flight in Seattle. (I have particularly fond memories of G-BOAG; in a previous post I mentioned flying through an electrical storm in late 1991 over Saudi Arabia, while returning from BKK-BAH to LHR. What I forgot to mention was the spectacle of DOZENS of fierce fires burning on the ground, towards our starboard horizon. These were Sadams oil fires, still burning in Kuwait. It made a sombre contrast to the amazing electrical spectacle right in front of us).
As far as low speed flying control activity was concerned, this was a combination of the fairly flexible outer wing sections, being buffeted by low speed turbulence (the wing tip tanks 5A & 7A also being empty), as well as some autostab inputs. This was perfectly normal, and part of the design our aircraft. However the development aircraft had even more flexible outer wing sections, which used to almost straighten up in high speed flight. However due to fatigue concerns, external lateral stiffeners were added to the underside of the wings during production of the airline aircraft. (these can be easily seen from underneath the wings, just outboard of the nacelles). Unfortunately these external stiffeners also resulted in over a one tonne fuel penalty to the production aircraft, due to increased weight, as well as higher drag in a critical part of the wing aerodynamic surface.
Dude
As far as your adventure goes, in the early days of Concorde operation there was an on-going issue of hydraulic seal failures. This led to the sort of thing that you described, where a major seal failure would occur, resulting in the loss of a main system. The standby Yellow system would be switched in to replace the failed one, and depending on the nature of the initial failure, could leak out of the same failed seal. (There were a couple of 'common areas', they were the intake spill door jack, and the Powered Flying Control Units; failures here could result in a double system fail). Your incident was almost certainly due to one of these cases. In the early 1990's the original Neoprene hydraulic seals were replaced with a new Viton GLT seal; this material had far superior age shrinking characteristics to Neoprene, and more or less cured the problem overnight. Eventually all the seals in each aircraft were replaced, and apart from a very few isolated cases, dual system losses were eliminated forever. Air France suffered a similar proportion of failures, however as their flying hours were a fraction of BA's, the effects were not as immediately apparent.
As far as far as the hydraulic contamination story goes, this happened in 1980 but involved one aircraft only, G-BOAG, but in it's original registration of G-BFKW. (having previously been on loan from British Aerospace, where it flew originally as a 'white tail' under this registration). The fragile nature of Concorde hydraulic fluid was not fully understood at this time, and as you say, a hydraulic drum dispenser had inadvertently been left exposed to the atmosphere, and had subsequently suffered water contamination, and this contaminated fluid had found it's way into G-BOAG. Now this hydraulic fluid, CHEVRON M2V has only two vices: One is that is extremely expensive, and the second is that it is highly susceptible to water contamination, EXTEMELY SO. If my memory serves me correctly, the maximum allowable level of water in the fluid is about 8ppm. (parts per million) and the fluid that was analysed after G-BOAG's problems was at about 30 ppm. The water deposits in the fluid gave the equivalent effect of 'rusting up' of critical hydraulic components. I was investigating an air intake control defect the previous day to the incident, but like everybody else had no idea that the real issue here was one of major systems contamination. We were all convinced that we had nailed the problem, only to find that the aircraft turned back on it's subsequent LHR-JFK sector with more serious problems, not only affecting the air intakes, but the artificial feel system also. It was now that we realised that there had to be a hydraulics problem here, and after fluid analysis, the awful truth was discovered. After this event, and the fragilities of M2V fluid were better understood, a strict regime of housekeeping was put in place in terms of fluid storage, and no such incidents with BA ever occurring again. The aircraft itself did not fly again for nine months, all components that were affected were removed from the aircraft and completely stripped and overhauled. Also all of the system hydraulic lines had to be completely purged, until there were no further traces of any contamination. After the aircraft was finally rectified, she successfully again returned to service with her new 'BA' registration of G-BOAG. However the following year, during a C Check, it was decided that due to spares shortages, and the closure of the LHR-BAH-SIN route, there just was not being enough work for seven aircraft, and therefore G-BOAG would be withdrawn from service. (In terms of spares, BA at the time for instance only had six sets of aircraft galleys, as aircraft went in for C checks the galley was 'robbed' to service the aircraft coming out of it's own C check). The aircraft was parked in a remote hangar, and was only visited when a component had to be 'robbed' for another Concorde, and the aircraft soon fell into disrepair, was filthy externally and became a really sad sight. Many people (not myself I might add) were adamant that G-BOAG would never fly again. However, in 1984 things had really started to improve for Concorde, with the charter business increasing and the LHR-JFK route in particular becoming a staggering success. It was decided that OAG would be returned to an airworthy condition. In 1985, with a fresh new interior, and with the new BA colour scheme, she was finally returned to service; and remained as one of the mainstays of the fleet right up to the end of Concorde services in October 2003. She now resides at the Boeing Museum of Flight in Seattle. (I have particularly fond memories of G-BOAG; in a previous post I mentioned flying through an electrical storm in late 1991 over Saudi Arabia, while returning from BKK-BAH to LHR. What I forgot to mention was the spectacle of DOZENS of fierce fires burning on the ground, towards our starboard horizon. These were Sadams oil fires, still burning in Kuwait. It made a sombre contrast to the amazing electrical spectacle right in front of us).
As far as low speed flying control activity was concerned, this was a combination of the fairly flexible outer wing sections, being buffeted by low speed turbulence (the wing tip tanks 5A & 7A also being empty), as well as some autostab inputs. This was perfectly normal, and part of the design our aircraft. However the development aircraft had even more flexible outer wing sections, which used to almost straighten up in high speed flight. However due to fatigue concerns, external lateral stiffeners were added to the underside of the wings during production of the airline aircraft. (these can be easily seen from underneath the wings, just outboard of the nacelles). Unfortunately these external stiffeners also resulted in over a one tonne fuel penalty to the production aircraft, due to increased weight, as well as higher drag in a critical part of the wing aerodynamic surface.
Dude

Last edited by M2dude; 3rd Sep 2010 at 00:07 .
4th Sep 2010, 10:49
permalink Post: 212
BRIT312
This story is totally hilarious, can't quite get this visual out of my head. ('100 KTS, POWER SET' sounds so boring in comparison).
 I never had the good fortune to meet any of the Braniff guys; sounds like there was certainly a character or two there. It really is a pity that their operation never really got a chance to expand into the proposed Pacific Rim service, who knows, it might really have done something.
I never had the good fortune to meet any of the Braniff guys; sounds like there was certainly a character or two there. It really is a pity that their operation never really got a chance to expand into the proposed Pacific Rim service, who knows, it might really have done something.
It's generally known that the BA aircraft were temporarily re-registered to facilitate Braniff's operation out of IAD to DFW; G-BOAA, B, D & E were re-registered from G-BOAA and so on, to G-N94AA etc. Being an older registration, G-BOAC was re-registered as G-N81AC. At IAD, the 'G' part of the registration was covered over, leaving a now perfect 'American' tail number. Only five aircraft were involved in the operation (at the time BA operated just six aircraft, G-BOAF was still at the manufacturers at Filton, and G-BFKW (later to become G-BOAG) was on loan from British Aerospace. In order for the necessary FAA certification, required for operation by a US airline, a modification package were required by the FAA. Some of these modifications seemed a little 'picky' and irrelevant at the time (they still do). However some modifications were certainly not in this category, and quite honestly should have been 'picked up' by the CAA & DGAC during original certification of the aircraft. As an example, if the flying controls had been operating on GREEN or BLUE hydraulics only (due to an indicated spool valve jam) and that particular hydraulic system was subsequently lost, there was originally no automatic switching to select the standby YELLOW system into the flying controls; the controls would have been completely unpowered until a manual selection was made by the pilot. . One of the 'FAA Mods' was to facilitate just that, so if this (extremely unlikely I grant you) scenario had occurred, then YELLOW would automatically been selected into the controls, and at no time would the controls have been in an unpowered state.
The Braniff operation ended in May 1980, due to heavy losses on the subsonic only route, and it's a rather sad irony that aircraft G-BOAF had been modified and reregistered at Filton, from it's original registration of G-BFKX to G-N94AF. Unfortunately the aircraft was delivered to BA in June 1980, one month too late to participate, and prior to delivery it's registration was converted to it's 'normal' British registration; all other aircraft also reverted to original registrations also.
ChristiaanJ
Not really, being the sad b****d that I am, I still remember the Concorde flare law of: h+5h. = 0, so it was fairly easy to work out the programmed descent rates. (I did have to check the final 1.7'/second figure though). The rest I'm afraid is straight out of this sad old memory of mine.
Bellerophon
A brilliant description of the mechanics of final approach. It's so easy for us mere mortals to forget just what an involved and skilled process it was, to fly, and in particular land our totally amazing aircraft.
Dude
Quote:
| Now the F/E had a couple of calls to make prior to V1 relating to how good the engines were performing the most important being at 100 kts, however before we got that far the Braniff F/E stood up in his harness and let out the cry " Gee Whiz look at the son of a bitch go". |
 I never had the good fortune to meet any of the Braniff guys; sounds like there was certainly a character or two there. It really is a pity that their operation never really got a chance to expand into the proposed Pacific Rim service, who knows, it might really have done something.
I never had the good fortune to meet any of the Braniff guys; sounds like there was certainly a character or two there. It really is a pity that their operation never really got a chance to expand into the proposed Pacific Rim service, who knows, it might really have done something.
It's generally known that the BA aircraft were temporarily re-registered to facilitate Braniff's operation out of IAD to DFW; G-BOAA, B, D & E were re-registered from G-BOAA and so on, to G-N94AA etc. Being an older registration, G-BOAC was re-registered as G-N81AC. At IAD, the 'G' part of the registration was covered over, leaving a now perfect 'American' tail number. Only five aircraft were involved in the operation (at the time BA operated just six aircraft, G-BOAF was still at the manufacturers at Filton, and G-BFKW (later to become G-BOAG) was on loan from British Aerospace. In order for the necessary FAA certification, required for operation by a US airline, a modification package were required by the FAA. Some of these modifications seemed a little 'picky' and irrelevant at the time (they still do). However some modifications were certainly not in this category, and quite honestly should have been 'picked up' by the CAA & DGAC during original certification of the aircraft. As an example, if the flying controls had been operating on GREEN or BLUE hydraulics only (due to an indicated spool valve jam) and that particular hydraulic system was subsequently lost, there was originally no automatic switching to select the standby YELLOW system into the flying controls; the controls would have been completely unpowered until a manual selection was made by the pilot. . One of the 'FAA Mods' was to facilitate just that, so if this (extremely unlikely I grant you) scenario had occurred, then YELLOW would automatically been selected into the controls, and at no time would the controls have been in an unpowered state.
The Braniff operation ended in May 1980, due to heavy losses on the subsonic only route, and it's a rather sad irony that aircraft G-BOAF had been modified and reregistered at Filton, from it's original registration of G-BFKX to G-N94AF. Unfortunately the aircraft was delivered to BA in June 1980, one month too late to participate, and prior to delivery it's registration was converted to it's 'normal' British registration; all other aircraft also reverted to original registrations also.
ChristiaanJ
Quote:
| Reading your description of the autoland, you must be quoting from documentation, no? |
Bellerophon
A brilliant description of the mechanics of final approach. It's so easy for us mere mortals to forget just what an involved and skilled process it was, to fly, and in particular land our totally amazing aircraft.
Dude

Last edited by M2dude; 4th Sep 2010 at 13:12 .
7th Sep 2010, 11:41
permalink Post: 255
Brit312
Right on the button as usual Brit312, the shortening jack DID just assit breaking of the geometric lock, it was the process of retraction alone that did the actual shortening. Humble aplologies to all for this age induced goof.

And as both yourself and EXWOK pointed out, Air France had a ni-cad based DC power system, the same as G-BOAG.
Dude
Quote:
|
Concorde's main landing gear consisted of 3 seperate metal castings . there was the normal two for the oleo and these two were fitted inside the outer casting, which was the one you could see.
As the gear retracted a mechanical linkage , which was driven by the gear's retraction movement, would lift the oleo assembly up into the outer casing, so shortening the length of the leg . If I remember the shortening jack was just to assist in breking the geometric lock of the linkage |

And as both yourself and EXWOK pointed out, Air France had a ni-cad based DC power system, the same as G-BOAG.
Dude

30th Sep 2010, 13:58
permalink Post: 499
As promised here are the answers to our trivia quiz.
Actually there were 14 (but if you are not necessarily a Concorde person, 13 is acceptable). There were '13 fuel tanks, numbered 1 - 11' as we used to tell all the visitors to the aircraft, (The wingtip tanks 5A & 7A making up the extra 2) PLUS a single small
scavenge tank
at the rear of the aircraft that was used to remove fuel from the vent lines and return this fuel via a transfer pump back to tank 3. (A fuel level sensor would trigger the pump with only 1 US Gallon of fuel in the tank). If the trim gallery became over-pressurised (ie tank 3 already full to the brim) an overflow relief valve (ORV) underneath the rear of the aircraft would open and dump the contents of the tank overboard. There was a flight deck indication if the scavenge pump was running in flight to give the crew an indication that a tank somewhere was probably over-filling and to take the appropriate action. There was one added goody about the ORV; If you were on the ground with the refuel door open and due to a refuelling overfill anywhere, fuel entered the scavenge tank, at 7 gallons the ORV would open and rapidly dump the fuel on the floor. For this reason a vent pipe and fuel drum was often placed underneath the ORV during high load refuels. If this was not fitted and you just happened to walk underneath the aircraft at the wrong moment during fuelling........

As a total aside to all this (or me going off on a tangent yet again) the fuel tanks themselves were gently air pressurised above 44,000' to around 2.2 PSIA. This was to prevent the beginnings of any boiling of the fuel in the tanks, due to the low ambient pressure/high fuel temperatures, causing pump cavitation. (Boiling itself could not occur much below 65,000'). A small NACA duct at the right side of the fin was used to supply the ram air for tank pressurisation, the two vent valves in the tail cone, one per trim gallery, closing off automatically at around 44,000', the pressure being controlled by a pneumatic valve, with full automatic over-pressure protection. OK sorry guys and gals, back to the answers:
This is the stinker.... there were 114 (although at entry into service there were 115!!). 100 passenger seats + 6 cabin crew seats + 5 flight deck seats (including the fold up seat in the aisle at the rear) PLUS 3 LOO SEATS (Originally 4 loos, the fourth loo being removed in the early 1980's).

50,189' and 530 KEAS, but we'll settle for anything around FL500 being correct.

Aircraft 216, G-BOAF, the last Concorde ever built. When 216 first flew in 1979 she was a variant 192 'British Unsold Aircraft' and was registered as G-BFKX. In late 1979, BA purchased the aircraft and it was subsequently converted to a Type 102 British Airways variant, and after modifications were complete, test flights were carried out from Filton under the registration of G-N94AF. This registration was to enable the aircraft to participate in the Braniff interchange between IAD and DFW, but when the Braniff Concorde adventure unfortunately ended in 1980, she was again re-registered to G-BOAF, this is how she was delivered to BA later that year.

Easy one this I hope; 60.000'. (As we've said before this limitation was imposed because of the dual window failure / emergency descent time consideration, not as a performance issue. On test flights 63,000' was routinely attained, and altitudes of up to 68,000' were achieved during development flying. (On her maiden flight, G-BOAB achieved 65,000' and Mach 2.04; the first British constructed Concorde to achieve Mach 2 on her maiden flight, and the ONLY one of the original five BA aircraft to achieve this).

Hopefully an easy one... there were TWELVE: 2 nose wheels, 8 main wheels and 2 tail wheels. (No, even I'm not nasty enough to include the wheels on the bar trolleys
 ). Oh, and there were 9 wheel brakes, one for each main wheel and as was mentioned in a previous post, a single steel disc brake for the nose wheels (the nose having a live axle), for automatic use during gear retraction only.
). Oh, and there were 9 wheel brakes, one for each main wheel and as was mentioned in a previous post, a single steel disc brake for the nose wheels (the nose having a live axle), for automatic use during gear retraction only.

Three modes; Blue electronic signalling, green electronic signalling and mechanical signalling. I suppose we COULD be pedantic here and include the Emergency Flight Control mode where even with a jammed control column/control wheel, strain gauges (and Safety Flight Control Computers of course) would still enable you to control the elevons.

OK, three basically. Up (Duh!), 5 degrees for taxi/take off and low speed flight and 12.5 degrees for landing. As ChristiaanJ quite rightly pointed out in an earlier post, the prototype (and pre-production) aircraft landing position was 17.5 degrees of droop. (In my view the nose of the aircraft looked a little like an armadillo in this extreme configuration).

In 1977 the new digital Plessey PVS 1580 Aircraft Integrated Data System was progressively fitted to the BA fleet, this being the first microprocessor application on Concorde, this application being followed in several other systems during the life of the aircraft. The 'final' applications being TCAS and the superb retrofitted Bendix RDR-4A weather radar system.

No we are not including torch batteries and emergency lights etc.
 There were a total of seven main power sources: 4 x 60KVA AC generators, one per engine, a single 40KVA hydraulically powered emergency generator and 2 lead acid (or ni-cad in the case of G-BOAG) main aircraft batteries. (Not a terribly Re-Volting question I hope).
There were a total of seven main power sources: 4 x 60KVA AC generators, one per engine, a single 40KVA hydraulically powered emergency generator and 2 lead acid (or ni-cad in the case of G-BOAG) main aircraft batteries. (Not a terribly Re-Volting question I hope).

I hope this quiz was fun and not too perplexing to any of you guys.
Dude
Quote:
| 1) How many fuel tanks were there on Concorde? |

As a total aside to all this (or me going off on a tangent yet again) the fuel tanks themselves were gently air pressurised above 44,000' to around 2.2 PSIA. This was to prevent the beginnings of any boiling of the fuel in the tanks, due to the low ambient pressure/high fuel temperatures, causing pump cavitation. (Boiling itself could not occur much below 65,000'). A small NACA duct at the right side of the fin was used to supply the ram air for tank pressurisation, the two vent valves in the tail cone, one per trim gallery, closing off automatically at around 44,000', the pressure being controlled by a pneumatic valve, with full automatic over-pressure protection. OK sorry guys and gals, back to the answers:

Quote:
| 2) How many seats were there? |

Quote:
| 3) At what approximate altitude and KNOTS EAS was Mach 2 achieved? |

Quote:
| 4) Only one BA Concorde had three different registrations, what was it? |

Quote:
| 5) What was the maximum permitted altitude in passenger service? |

Quote:
| 6) How many wheels on the aircraft |
 ). Oh, and there were 9 wheel brakes, one for each main wheel and as was mentioned in a previous post, a single steel disc brake for the nose wheels (the nose having a live axle), for automatic use during gear retraction only.
). Oh, and there were 9 wheel brakes, one for each main wheel and as was mentioned in a previous post, a single steel disc brake for the nose wheels (the nose having a live axle), for automatic use during gear retraction only.

Quote:
| 7) How many flying control modes were there? |

Quote:
| 8) How many positions of nose droop were there? |

Quote:
| 9) What was the first microprocessor application on the aircraft? |

Quote:
| 10) How many main electrical sources were there? |
 There were a total of seven main power sources: 4 x 60KVA AC generators, one per engine, a single 40KVA hydraulically powered emergency generator and 2 lead acid (or ni-cad in the case of G-BOAG) main aircraft batteries. (Not a terribly Re-Volting question I hope).
There were a total of seven main power sources: 4 x 60KVA AC generators, one per engine, a single 40KVA hydraulically powered emergency generator and 2 lead acid (or ni-cad in the case of G-BOAG) main aircraft batteries. (Not a terribly Re-Volting question I hope).

I hope this quiz was fun and not too perplexing to any of you guys.
Dude

30th Sep 2010, 15:03
permalink Post: 500
I copied this off M2dude's post a couple of days ago, and tried to answer it all offline without cheating by looking up the answers elsewhere.
1) How many fuel tanks were there on Concorde?
LOL... 13.
I suppose that, for the same reason there was no row 13 in the cabin, somebody decided to name two of the tanks "5A" and "7A", rather than call the tail trim tank (named no.11) number 13.
Yes, I forgot the scavenge tank.
And since it was "BA Concordes only" I didn't want to add the hydrazine tank on the two preprod and the two certification aircraft.
2) How many seats were there?
Good question.
As Nick asked, which seats?
Nominally there were 100 pax seats in the cabin, although originally up to 127 were certified.
Five (three plus two jump seats) in the cockpit.
Cabin seats for the cabin crew.... I honestly don't know. Seven?
Wrong twice... six cabin crew seats, AND I forgot to count the loos!
3) At what approximate altitude and KNOTS EAS was Mach 2 achieved?
Roughly, FL500 and 530 kts.
But not being a pilot I had to check an instant on my flight envelope crib sheet, which I have at hand all the time.....
It seemed pointless to be TOO precise, because that assumed ISA and creeping exactly up the right edge of the envelope.
4) Only one BA Concorde had three different registrations, what was it?
Without looking it up, no idea. My guess is G-BOAF, with a white-tail reg, a "British" reg, and a pseudo-American reg.
IIRC, G-BOAG never had a pseudo-American reg, but I'm not sure without looking it up.
Brain not completely addled, then.
5) What was the maximum permitted altitude in passenger service?
FL600, as certified.
6) How many wheels on the aircraft?
Twelve, if you count the two Spitfire wheels at the back
7) How many flying control modes were there?
Four. Blue, green, mechanical and ... what did we call it? Control jam, CWS?
Ah, thanks, Emergency Flight Control. I always considered it as a separate mode, even if it was virtually never used.
8) How many positions of nose droop were there?
Four. 0\xb0, 5\xb0, 12.5\xb0 and 17.5\xb0 (the latter only on the prototypes, and purely mechanically, after removing a stop, on the other aircraft).
9) What was the first microprocessor application on the aircraft?
No idea... you (M2dude) mentioned a Plessey data acquisition system?
It was after "my time"...
10) How many main electrical sources were there?
Again, not sure... You're presumably are talking about primary sources.
There was an AC constant-drive generator on each engine.
Then there were two DC batteries.
And IIRC there was an AC generator running off the RAT hydraulic generator when pillar came to post.
Reading M2dude's answer, I suppose the emergency generator just ran off the hydraulics, not specifically off the RAT. Far more logical.
Nice one, M2dude!
And certainly not all trivia!
CJ
1) How many fuel tanks were there on Concorde?
LOL... 13.
I suppose that, for the same reason there was no row 13 in the cabin, somebody decided to name two of the tanks "5A" and "7A", rather than call the tail trim tank (named no.11) number 13.
Yes, I forgot the scavenge tank.
And since it was "BA Concordes only" I didn't want to add the hydrazine tank on the two preprod and the two certification aircraft.
2) How many seats were there?
Good question.
As Nick asked, which seats?
Nominally there were 100 pax seats in the cabin, although originally up to 127 were certified.
Five (three plus two jump seats) in the cockpit.
Cabin seats for the cabin crew.... I honestly don't know. Seven?
Wrong twice... six cabin crew seats, AND I forgot to count the loos!
3) At what approximate altitude and KNOTS EAS was Mach 2 achieved?
Roughly, FL500 and 530 kts.
But not being a pilot I had to check an instant on my flight envelope crib sheet, which I have at hand all the time.....
It seemed pointless to be TOO precise, because that assumed ISA and creeping exactly up the right edge of the envelope.
4) Only one BA Concorde had three different registrations, what was it?
Without looking it up, no idea. My guess is G-BOAF, with a white-tail reg, a "British" reg, and a pseudo-American reg.
IIRC, G-BOAG never had a pseudo-American reg, but I'm not sure without looking it up.
Brain not completely addled, then.
5) What was the maximum permitted altitude in passenger service?
FL600, as certified.
6) How many wheels on the aircraft?
Twelve, if you count the two Spitfire wheels at the back
7) How many flying control modes were there?
Four. Blue, green, mechanical and ... what did we call it? Control jam, CWS?
Ah, thanks, Emergency Flight Control. I always considered it as a separate mode, even if it was virtually never used.
8) How many positions of nose droop were there?
Four. 0\xb0, 5\xb0, 12.5\xb0 and 17.5\xb0 (the latter only on the prototypes, and purely mechanically, after removing a stop, on the other aircraft).
9) What was the first microprocessor application on the aircraft?
No idea... you (M2dude) mentioned a Plessey data acquisition system?
It was after "my time"...
10) How many main electrical sources were there?
Again, not sure... You're presumably are talking about primary sources.
There was an AC constant-drive generator on each engine.
Then there were two DC batteries.
And IIRC there was an AC generator running off the RAT hydraulic generator when pillar came to post.
Reading M2dude's answer, I suppose the emergency generator just ran off the hydraulics, not specifically off the RAT. Far more logical.
Nice one, M2dude!
And certainly not all trivia!
CJ
9th Oct 2010, 17:50
permalink Post: 538
DavvaP
,
No I would not say you're "far too dumb".... yours are valid questions.
You're right, "it would have been too big an undertaking for too little benefit".
Don't forget the history... it was the governments that financed development, manufacture and (initially) operations.
By the time the last few aircraft came off the production line they were already unsaleable 'white tails'.
Now, the "B" modifications to the wing were quite major (droop leading edge, extended wingtip, other tweaks) and to reftrofit them would have been difficult and costly.
The "B" engine had a larger frontal diameter, so the engine nacelles would have had to be redesigned and re-manufactured.
All those modifications would then have to have been revalidated and recertified, then applied to each of the aircraft, plus the manufacture of new spares, etc.
Still saddled with five unsold aircraft at the time, there was no way the governments were going to finance such a major upgrade.
As to G-BOAG...
Applying some or all of the modifications to G-BOAG only would have been pure folly, because it would have meant a large separate spares store, revalidation and recertification, separate documentation, etc. etc. all for one aircraft.
Finally, the story doesn't tell if Rolls Royce ever got as far as running a prototype "B" type engine on a test bed. Certainly, none were ever manufactured.
CJ
No I would not say you're "far too dumb".... yours are valid questions.
You're right, "it would have been too big an undertaking for too little benefit".
Don't forget the history... it was the governments that financed development, manufacture and (initially) operations.
By the time the last few aircraft came off the production line they were already unsaleable 'white tails'.
Now, the "B" modifications to the wing were quite major (droop leading edge, extended wingtip, other tweaks) and to reftrofit them would have been difficult and costly.
The "B" engine had a larger frontal diameter, so the engine nacelles would have had to be redesigned and re-manufactured.
All those modifications would then have to have been revalidated and recertified, then applied to each of the aircraft, plus the manufacture of new spares, etc.
Still saddled with five unsold aircraft at the time, there was no way the governments were going to finance such a major upgrade.
As to G-BOAG...
Applying some or all of the modifications to G-BOAG only would have been pure folly, because it would have meant a large separate spares store, revalidation and recertification, separate documentation, etc. etc. all for one aircraft.
Finally, the story doesn't tell if Rolls Royce ever got as far as running a prototype "B" type engine on a test bed. Certainly, none were ever manufactured.
CJ
16th Oct 2010, 14:47
permalink Post: 577
questions
Humble SLF here, hope it is ok to have a stab at the questions, mods please feel free to delete if necessary.
1) How many Concorde airframes were built?
22, 20 that flew and 2 test frames
2) As far as the British constructed aircraft went, name the destinations that were served?. Regular flight numbers only, excludes charters etc.
New York, Washington, Miami, Barbados, Toronto, Bahrain and Singapore, no British registered aircraft ever operated to or form Dallas, should not forget BAs most popular destination of all time-London
3) What was the departure time for the ORIGINAL morning LHR-JFK Concorde services? (Not called the BA001 then either).
0930-Local
4) Further to question 3 above, what WERE the original flight numbers for the BA001 and BA003? (The morning and evening LHR-JFK services?).
193 & 195 respectiveley
5) There were no less than FORTY SIX fuel pumps on Concorde. What was the breakdown for these? (Clue; don't forget the scavange pump ).
Pass
6) What was the only development airframe to have a TOTALLY unique shape?
101, G-AXDN
7) This one is particularly aimed at ChristiaanJ. What was the total number of gyros on the aircraft?
pass
8) How many wheel brakes?
8
9) What Mach number was automatic engine variable intake control enabled?
1.3
10) Above each bank of engine instruments were three lights, a blue, a green and an amber. What did they each signify?
Not sure here, best guess -green was part of the take-off moniter -red failure-blue reverse
11) At what airfied were the first BA crew base training details held?
Prestwick, shannon, and one in France
12) What LHR runways did Concorde use for landing and take-off? (Trick question, not as obvious as it might seem).
28L , 28R, 27L, 27R, 9L, 9R 10L 10R, 23
13) What operator had serious plans to operate Concorde from SNN to JFK in the early 1980's?
Fed-ex
14) What development aircraft did not exceed Mach 2 until fifteen months after her maiden flight?
214? G-BFKW
1) How many Concorde airframes were built?
22, 20 that flew and 2 test frames
2) As far as the British constructed aircraft went, name the destinations that were served?. Regular flight numbers only, excludes charters etc.
New York, Washington, Miami, Barbados, Toronto, Bahrain and Singapore, no British registered aircraft ever operated to or form Dallas, should not forget BAs most popular destination of all time-London
3) What was the departure time for the ORIGINAL morning LHR-JFK Concorde services? (Not called the BA001 then either).
0930-Local
4) Further to question 3 above, what WERE the original flight numbers for the BA001 and BA003? (The morning and evening LHR-JFK services?).
193 & 195 respectiveley
5) There were no less than FORTY SIX fuel pumps on Concorde. What was the breakdown for these? (Clue; don't forget the scavange pump ).
Pass
6) What was the only development airframe to have a TOTALLY unique shape?
101, G-AXDN
7) This one is particularly aimed at ChristiaanJ. What was the total number of gyros on the aircraft?
pass
8) How many wheel brakes?
8
9) What Mach number was automatic engine variable intake control enabled?
1.3
10) Above each bank of engine instruments were three lights, a blue, a green and an amber. What did they each signify?
Not sure here, best guess -green was part of the take-off moniter -red failure-blue reverse
11) At what airfied were the first BA crew base training details held?
Prestwick, shannon, and one in France
12) What LHR runways did Concorde use for landing and take-off? (Trick question, not as obvious as it might seem).
28L , 28R, 27L, 27R, 9L, 9R 10L 10R, 23
13) What operator had serious plans to operate Concorde from SNN to JFK in the early 1980's?
Fed-ex
14) What development aircraft did not exceed Mach 2 until fifteen months after her maiden flight?
214? G-BFKW
27th Oct 2010, 22:33
permalink Post: 616
Mike-Bracknell
It is not nonsense, and you are quite at liberty to post here. Wow, that's still quite a question though Mike. There are two TECHNICAL issues that overshadow all others, namely airframe corrosion and hydraulic system deterioration. Unfortunately none of the BA aircraft were stored inside from the outset, so we have a real issue here as far as corrosion goes, plus all the hydraulic systems were drained, resulting in seal drying out and probable moisture ingress into the 3 systems. But given sufficient funds (and assuming you find an organisation to take over design responsibility from Airbus;
ironic when you consider that without Concorde there would almost certainly have been no such organisation
) there is still no technical reason why the problems (and there are dozens of other problems to consider) could not be overcome, the money side of things is another matter
Looking first at the French fleet, the main candidate for restoration to flight status would be F-BTSD at Le Bourget. Not only has this aircraft been lovingly cared for and stored INSIDE, but the aircraft has had several systems (including the Green hydraulic system) powered and reservoirs not drained.
The British story is less clear; G-BOAA in East Fortune was effectively killed when the wings were cut off for transportation, so that one is out of the question. G-BOAB, the last and only Concorde at LHR has been left to rot outside, in fact holes were even drill in the fuselage to drain water, so this one is a no no too. G-BOAC at Manchester, now the oldest surviving production aircraft was initially stored outside, but now resides in a purpose built exhibition 'hangar'. Now she COULD be a potential candidate for consideration; when I last saw her just over a year ago she was absolutely pristine; a testament to the team that have been caring for her there. G-BOAD, stored next to the USS Intrepid in New York, we can probably forget, due to having been exposed to 7 years worth of salt water corrosion from the Hudson River. (Also, while she was temporarily stored in New Jersey a couple of years ago, some IDIOT in a truck bent the whole nose section when he hit her. The radome was smashed (replaced with a rather clever fibreglass fabrication) and the nose straightened with a blow-torch and hammer (I am not joking!!). G-BOAE at Grantley Adams airport in Barbados has been stored under cover for much of the time; provided she has not suffered too much from the wam damp atmosphere of Barbados, well she could be a potential candiitate too. G-BOAF in Filton, well PROVIDED she is still OK after her 'removal from public view' experience could also be a potential candidate also. And finally, G-BOAG in Seattle; well she had been left outside, right next to a highway (and close to a truck stop too). She did not look too good the last time I saw her; the undercarriage barrels werer all brown and discoloured and the paintwork was completely dull and matte. (She had a new paint job not too long before retirement too). So out of the 'BA Seven', I PERSONALLY would go for G-BOAF, G-BOAC or G-BOAG.
As I have said often here before, it is EXTREMELY unlikely that what you, Mike, suggest will ever happen, but in spite of what others might say, IT IS NOT IMPOSSIBLE. My own gut feeling is a resounding 'no', but I could be wrong, . (And NO ONE would be happier than I if I am wrong; I was with the BA aircraft through construction, flight testing and the entire service life with BA).
As for the cost? It really is a case of 'how long is a piece of string', but for 2 aircraft we could be looking in excess of $100 or more, who knows?
But as the Everly Brothers used to sing 'All I have to do is dream.'
Keep posting Mike.
Dude .
.
Quote:
| IF funding were secured to get 1 Concorde from each fleet into the air again, which one out of each fleet would be the easiest to return to service, given what has gone on since retirement? Also, a subpoint, does anyone have any finger-in-the-air figures as to how much cost it would take and whether there's any fundamental issues that would need to be sorted aside from the airworthiness certificate etc. |
Looking first at the French fleet, the main candidate for restoration to flight status would be F-BTSD at Le Bourget. Not only has this aircraft been lovingly cared for and stored INSIDE, but the aircraft has had several systems (including the Green hydraulic system) powered and reservoirs not drained.
The British story is less clear; G-BOAA in East Fortune was effectively killed when the wings were cut off for transportation, so that one is out of the question. G-BOAB, the last and only Concorde at LHR has been left to rot outside, in fact holes were even drill in the fuselage to drain water, so this one is a no no too. G-BOAC at Manchester, now the oldest surviving production aircraft was initially stored outside, but now resides in a purpose built exhibition 'hangar'. Now she COULD be a potential candidate for consideration; when I last saw her just over a year ago she was absolutely pristine; a testament to the team that have been caring for her there. G-BOAD, stored next to the USS Intrepid in New York, we can probably forget, due to having been exposed to 7 years worth of salt water corrosion from the Hudson River. (Also, while she was temporarily stored in New Jersey a couple of years ago, some IDIOT in a truck bent the whole nose section when he hit her. The radome was smashed (replaced with a rather clever fibreglass fabrication) and the nose straightened with a blow-torch and hammer (I am not joking!!). G-BOAE at Grantley Adams airport in Barbados has been stored under cover for much of the time; provided she has not suffered too much from the wam damp atmosphere of Barbados, well she could be a potential candiitate too. G-BOAF in Filton, well PROVIDED she is still OK after her 'removal from public view' experience could also be a potential candidate also. And finally, G-BOAG in Seattle; well she had been left outside, right next to a highway (and close to a truck stop too). She did not look too good the last time I saw her; the undercarriage barrels werer all brown and discoloured and the paintwork was completely dull and matte. (She had a new paint job not too long before retirement too). So out of the 'BA Seven', I PERSONALLY would go for G-BOAF, G-BOAC or G-BOAG.
As I have said often here before, it is EXTREMELY unlikely that what you, Mike, suggest will ever happen, but in spite of what others might say, IT IS NOT IMPOSSIBLE. My own gut feeling is a resounding 'no', but I could be wrong, . (And NO ONE would be happier than I if I am wrong; I was with the BA aircraft through construction, flight testing and the entire service life with BA).
As for the cost? It really is a case of 'how long is a piece of string', but for 2 aircraft we could be looking in excess of $100 or more, who knows?
But as the Everly Brothers used to sing 'All I have to do is dream.'
Keep posting Mike.
Dude
 .
.
5th Nov 2010, 11:56
permalink Post: 663
I have to admit that some of the subsonic fuel burn figures for Concorde were truly eye watering, and without massive engine and airframe modifications there was precious little in service that could be done to improve things. Paradoxically improvements to the
supersonic
efficiency of the powerplant were easier to implement, and several modifications were implemented, tried or proposed to improve fuel burn:
Way back in the late 1970's we did a major modification to the intakes that increased capture area by 2.5% and gave us typically a 1.6% improvement in trans-Atlantic fuel burn, and although this was our biggest performance improvement modification, there were more:
The famous elevon and rudder trailing edge extension modifications (that due to poor design, produced in later life the water ingress induced honeycomb failures) together with the re-profiled fin leading edge modification, I never saw the performance gains quantified (anyone have any ideas?).
Can anyone here remember the riblet trial? In the mid 1990's Airbus supplied 'stick on' plastic riblets, applied to various areas on the under-side of the wing on G-BOAG. These riblets had very fine undulations moulded into the surface; the idea being that as the air flowed through and around the riblet patches, boundary layer turbulence, and hence induced drag would be reduced. Now, the performance gains (if any) were never quantified, mainly because the riblet patches either peeled off or the surface deteriorated with the continuous thermal cycle. (I was over in JFK when the aircraft first arrived after having the riblets fitted, and as the crew were trying to proudly show me these amazing aerodynamic devices, they were sadly embarassed, as several had dissapeared in the course of a single flight).
There was one modification, proposed by Rolls Royce in the late 1990's that did have quite a lot of potential; this was to increase the engine N1 by around 1.5%. This would have had the effect of increasing engine mass flow and therefore reducing the drag inducing spill of supersonic air over the lower lip of the intake. Depending on the temperature, the performance gains were in the order of a 1.5% improvement in fuel burn at ISA Plus upper atmosphere temperatures ('normal' LHR-JFK) to none at all at significant ISA Minus temperatures (LHR -BGI). The modifacation had been trialed on G-BBDG before her retirement in the early eighties, and was proven in terms of performance enhancement and engine stability. In order to keep TET at the pre-modification level, there was a small increase in N2 commanded also. (The higher N1 required an increase in primary nozzle area, reducing TET). The main reason for the modification not being implemented was one of cost; The Ultra Electronics Engine Control Units were analog units, and the modification was a simple replacement of two resistors per unit. However because ultimate mass flow limitation was also controll by the digital AICU (built by British Aerospace Guided Weapons Division) the cost of getting a software update for this exremely 'mature' unit was found to be prohibitive.
A certain 'brainy' SEO and myself were working on a modification to improve fuel burn on ISA minus sectors. The idea was to force the autopilot, in Max Cruise at low temperatures only , to fly the aircraft close to Mmo, rather than at Max Cruise speed of Mach 2 - 2.02; this would have given us gains of up to 1%, depending on the temperature. The basic electronics involved for the modification were relatively straightforward, but it was never pursued due to the complexity of dealing with temperature shears and the cost of certification.
Dude
Way back in the late 1970's we did a major modification to the intakes that increased capture area by 2.5% and gave us typically a 1.6% improvement in trans-Atlantic fuel burn, and although this was our biggest performance improvement modification, there were more:
The famous elevon and rudder trailing edge extension modifications (that due to poor design, produced in later life the water ingress induced honeycomb failures) together with the re-profiled fin leading edge modification, I never saw the performance gains quantified (anyone have any ideas?).
Can anyone here remember the riblet trial? In the mid 1990's Airbus supplied 'stick on' plastic riblets, applied to various areas on the under-side of the wing on G-BOAG. These riblets had very fine undulations moulded into the surface; the idea being that as the air flowed through and around the riblet patches, boundary layer turbulence, and hence induced drag would be reduced. Now, the performance gains (if any) were never quantified, mainly because the riblet patches either peeled off or the surface deteriorated with the continuous thermal cycle. (I was over in JFK when the aircraft first arrived after having the riblets fitted, and as the crew were trying to proudly show me these amazing aerodynamic devices, they were sadly embarassed, as several had dissapeared in the course of a single flight).

There was one modification, proposed by Rolls Royce in the late 1990's that did have quite a lot of potential; this was to increase the engine N1 by around 1.5%. This would have had the effect of increasing engine mass flow and therefore reducing the drag inducing spill of supersonic air over the lower lip of the intake. Depending on the temperature, the performance gains were in the order of a 1.5% improvement in fuel burn at ISA Plus upper atmosphere temperatures ('normal' LHR-JFK) to none at all at significant ISA Minus temperatures (LHR -BGI). The modifacation had been trialed on G-BBDG before her retirement in the early eighties, and was proven in terms of performance enhancement and engine stability. In order to keep TET at the pre-modification level, there was a small increase in N2 commanded also. (The higher N1 required an increase in primary nozzle area, reducing TET). The main reason for the modification not being implemented was one of cost; The Ultra Electronics Engine Control Units were analog units, and the modification was a simple replacement of two resistors per unit. However because ultimate mass flow limitation was also controll by the digital AICU (built by British Aerospace Guided Weapons Division) the cost of getting a software update for this exremely 'mature' unit was found to be prohibitive.
A certain 'brainy' SEO and myself were working on a modification to improve fuel burn on ISA minus sectors. The idea was to force the autopilot, in Max Cruise at low temperatures only , to fly the aircraft close to Mmo, rather than at Max Cruise speed of Mach 2 - 2.02; this would have given us gains of up to 1%, depending on the temperature. The basic electronics involved for the modification were relatively straightforward, but it was never pursued due to the complexity of dealing with temperature shears and the cost of certification.

Dude

Last edited by M2dude; 5th Nov 2010 at 15:49 .
28th Nov 2010, 17:27
permalink Post: 799
ChristiaanJ
There is THIS link from Gordon Roxborough's superb 'ConncordeSST site' CONCORDE SST : 10th Anniversary
As you can see the event occured on Christmas Eve in 1985. As you can see from the video, Capt John Hutchinson was also aboard G-BOAG as a commentator, the F/O being John 'Noj' White. (After leaving the fleet when he got his command, Noj eventually returned to Concorde many years later as Capt Noj).
At the bottom of the web page I am 99% sure that Gordon got it wrong when he said that the reason that there were only 6 aircraft for the Boxing day 'group photo' was that the seventh aircraft was in the paint shop. I was there when we did the photo shoot, and I am pretty sure the only reason we never had aircraft 7 was that it was in JFK.
CAAAD
I wouldn't be at all surprised (the Ultra ECA was a real steam powered piece of kit) but we always managed to get obsolete/obsolescent electron component somewhow. I remember when we test flew the Plessey (I think) digital ECA on G-BBDG in the late 1970's it was a fraction of the size, ran cooler and the engine parameters were more stable too. Such a pity that we never went down that road for the production aircraft.
Regards
Dude
There is THIS link from Gordon Roxborough's superb 'ConncordeSST site' CONCORDE SST : 10th Anniversary
As you can see the event occured on Christmas Eve in 1985. As you can see from the video, Capt John Hutchinson was also aboard G-BOAG as a commentator, the F/O being John 'Noj' White. (After leaving the fleet when he got his command, Noj eventually returned to Concorde many years later as Capt Noj).
At the bottom of the web page I am 99% sure that Gordon got it wrong when he said that the reason that there were only 6 aircraft for the Boxing day 'group photo' was that the seventh aircraft was in the paint shop. I was there when we did the photo shoot, and I am pretty sure the only reason we never had aircraft 7 was that it was in JFK.
CAAAD
Quote:
| Dude - I think basic engine hardware was in good supply, but there were concerns about the control amplifier component availability. |
Regards
Dude

29th Nov 2010, 13:35
permalink Post: 810
speedbirdconcorde
5 seconds I know, but it does at least compensate for my other screen hoggings.
Some really nice shots of G-BOAG and the SR71. (I particularly love the 'business end' shot of the J-58, showing the 4 afterburner rings).
I last visited OAG in Seattle about 5 years ago and the exterior had really suffered from the elements, being parked right next to a highway near one of the most beautiful but wettest cities in the USA. (Boeing told me that they were planning a re-paint, don't know if it ever happened though). The interior however was absolutely immaculate, thanks to the pre-conditioned air being pumped through the entire fuselage. (Now THAT'S the way to do it ).
).
And as for the last photo.....



 (I laughed so much I almost fell of the chair).
(I laughed so much I almost fell of the chair).

1965 BEA
Nice clip, pity it's an ambedded Flash movie. It is at a good resolution however, if you zoom in the web page it's really quite good quality.
Regards
Dude
5 seconds I know, but it does at least compensate for my other screen hoggings.

Some really nice shots of G-BOAG and the SR71. (I particularly love the 'business end' shot of the J-58, showing the 4 afterburner rings).
I last visited OAG in Seattle about 5 years ago and the exterior had really suffered from the elements, being parked right next to a highway near one of the most beautiful but wettest cities in the USA. (Boeing told me that they were planning a re-paint, don't know if it ever happened though). The interior however was absolutely immaculate, thanks to the pre-conditioned air being pumped through the entire fuselage. (Now THAT'S the way to do it
 ).
).
And as for the last photo.....




 (I laughed so much I almost fell of the chair).
(I laughed so much I almost fell of the chair).

1965 BEA
Nice clip, pity it's an ambedded Flash movie. It is at a good resolution however, if you zoom in the web page it's really quite good quality.

Regards
Dude

Last edited by M2dude; 29th Nov 2010 at 13:47 .
11th Dec 2010, 16:23
permalink Post: 852
Hi Galaxy Flyer -
When I first got the beast on my licence it was recorded as 'Concorde Series 102 & variant'.
(Translates as British-built series plus s/no. 214, aka G-BOAG)
These days it appears as just 'Concorde'. (I'm surprised it still appears at all since the type isn't current on the register).
It's a while since I filed a flt plan for a Concorde sector, but recall that it was entered as 'CONC'.
ATB
When I first got the beast on my licence it was recorded as 'Concorde Series 102 & variant'.
(Translates as British-built series plus s/no. 214, aka G-BOAG)
These days it appears as just 'Concorde'. (I'm surprised it still appears at all since the type isn't current on the register).
It's a while since I filed a flt plan for a Concorde sector, but recall that it was entered as 'CONC'.
ATB
15th Jan 2011, 10:59
permalink Post: 1100
A Journey Back In Time !!
OK, here is a photo that I took at Fairford in November 1976. I'd just had my very first Concorde flight on a brand new G-BOAD, and took this flight deck photo in the hangar later that afternoon (the doors are open hence the late afternoon Cotswold sky. The point of this rather poor (sorry guys, I was young for goodness sake) photo is to look at just how subtly different the 1976 flight deck WAS.
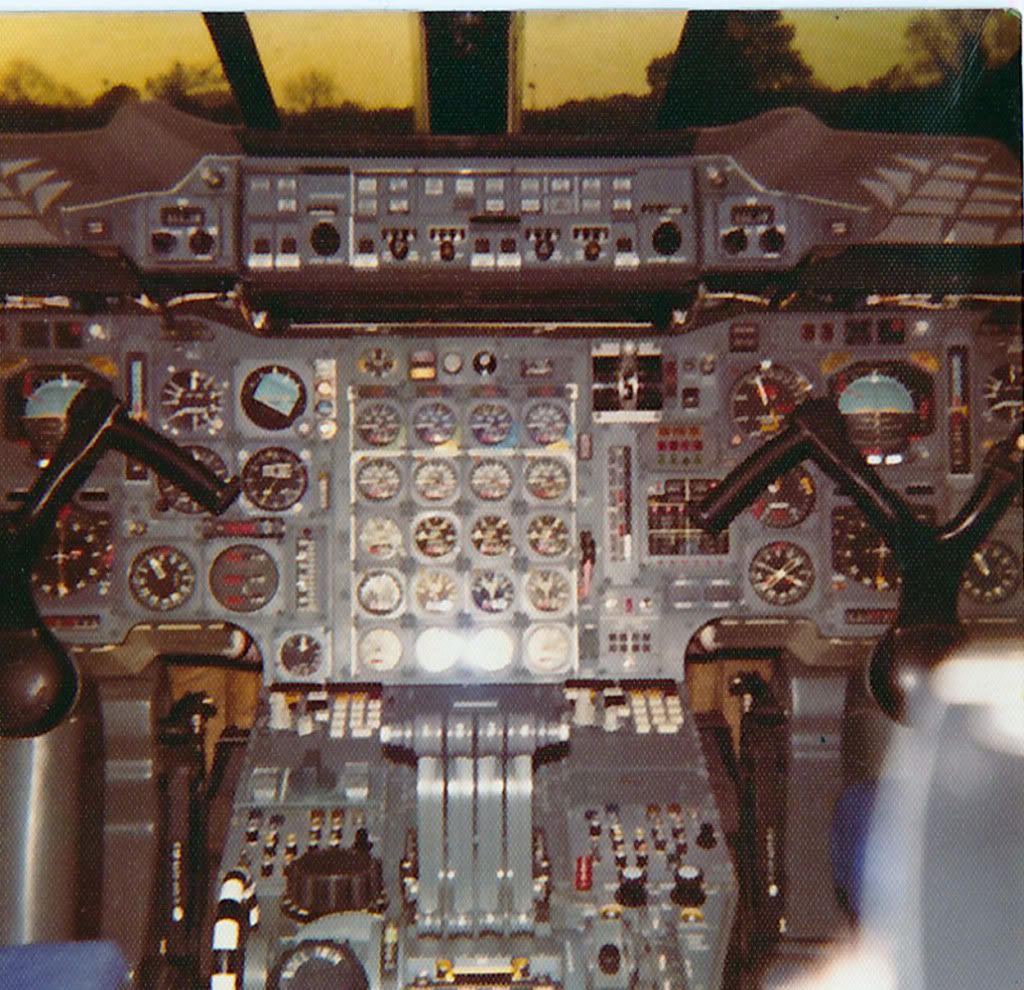
The first thing I know EXWOK and BELLEROPHON will (maybe) notice is that originally OAD had a 'normal colour' electroluminescent light plate on the visor indication panel. (If I remember rightly (it was a million years ago chaps) when this one 'stopped lighting' we could not get a replacement and had to rob 202 (G-BBDG) at Filton; this one being the same black development aircraft colour that OAD has to this day.
The OTHER first thing that you may notice is the Triple Temperature Indicator on the captains dash panel. (The first officer had his in in similar position). These got moved around (twice in the end) when TCAS was installed in the mid-90's. It was amazing just how much equipment got moved around over the years, in order to 'shoe-horn in' various bits of extra equimpent.
The cabin altimeter here fitted just above the #1 INS CDU also got moved (to the centre consul) when the FAA 'Branniff' modifications were embodied later in the 70's. It's spot got occupied by a standy altimeter mandated by the FAA but this was removed after Branniff ceased flying Concorde; the cabin altimeter returning to it's former home. The REALLY observant will notice that there is neither an Autoland Ca3/Cat2 identifier on the AFCS panel (glued on by BA at LHR) or the famous and precision built 'Reheat Capabilty Indicator' flip down plate fitted to the centre dash panel a few years later by BA.
Also not shown here, as they were buyer furnished equipment also fitted at on delivery LHR, are the two ADEUs (Automatic Data Entry Units, or INS Card readers). These were located immediatel aft of the CDU's and were used for bulk waypoint loading ('bulk' being 9, the most that the poor old Delco INU memory could handle). These were removed in the mid 90's when the Navigation Database was fitted to Concorde INUs, and bulk loading then was achieved by simply tapping in a 2 digit code. (Hardly the elegence of FMS, but still very elegent in comparison with the ADEU's, and worked superbly). A little note about these ADEU things; You inserted this rather large optically read paper data card into the thing and the motor would suck the unsuspecting card in. As often as not the ADEU would chew the card up and spit the remnants out, without reading any data, or not even bother spitting out the remnants at all. Removing these things FINALLY when the INUs were modified was absolute joy!!
ps. When G-BOAG (then G-BFKW) was delivered in 1980 it had neither any of the Branniff mods or ADEUs fitted. (Also the INS was not wired for DME updating). This meant that obviously she could not fly IAD-DFW with Branniff but also she could not do LHR-BAH either, because of the lack ADEUs. (You could not manually insert waypoints quick enough over the 'Med', or so the guys told me. So for the first few years good old FKW/OAG just used to plod between LHR and JFK. And plod she did, superbly. She never did get the ADEUs (not necessary thank goodness when the INUs got modified) but we wired in DME updating and so she could navigate around with the best of them.
My gosh I do prattle on, sorry guys.
Best regards
Dude
PS Welcome back Landlady, hope you've recovered from your fall XXXX
The first thing I know EXWOK and BELLEROPHON will (maybe) notice is that originally OAD had a 'normal colour' electroluminescent light plate on the visor indication panel. (If I remember rightly (it was a million years ago chaps) when this one 'stopped lighting' we could not get a replacement and had to rob 202 (G-BBDG) at Filton; this one being the same black development aircraft colour that OAD has to this day.
The OTHER first thing that you may notice is the Triple Temperature Indicator on the captains dash panel. (The first officer had his in in similar position). These got moved around (twice in the end) when TCAS was installed in the mid-90's. It was amazing just how much equipment got moved around over the years, in order to 'shoe-horn in' various bits of extra equimpent.
The cabin altimeter here fitted just above the #1 INS CDU also got moved (to the centre consul) when the FAA 'Branniff' modifications were embodied later in the 70's. It's spot got occupied by a standy altimeter mandated by the FAA but this was removed after Branniff ceased flying Concorde; the cabin altimeter returning to it's former home. The REALLY observant will notice that there is neither an Autoland Ca3/Cat2 identifier on the AFCS panel (glued on by BA at LHR) or the famous and precision built 'Reheat Capabilty Indicator' flip down plate fitted to the centre dash panel a few years later by BA.
Also not shown here, as they were buyer furnished equipment also fitted at on delivery LHR, are the two ADEUs (Automatic Data Entry Units, or INS Card readers). These were located immediatel aft of the CDU's and were used for bulk waypoint loading ('bulk' being 9, the most that the poor old Delco INU memory could handle). These were removed in the mid 90's when the Navigation Database was fitted to Concorde INUs, and bulk loading then was achieved by simply tapping in a 2 digit code. (Hardly the elegence of FMS, but still very elegent in comparison with the ADEU's, and worked superbly). A little note about these ADEU things; You inserted this rather large optically read paper data card into the thing and the motor would suck the unsuspecting card in. As often as not the ADEU would chew the card up and spit the remnants out, without reading any data, or not even bother spitting out the remnants at all. Removing these things FINALLY when the INUs were modified was absolute joy!!
ps. When G-BOAG (then G-BFKW) was delivered in 1980 it had neither any of the Branniff mods or ADEUs fitted. (Also the INS was not wired for DME updating). This meant that obviously she could not fly IAD-DFW with Branniff but also she could not do LHR-BAH either, because of the lack ADEUs. (You could not manually insert waypoints quick enough over the 'Med', or so the guys told me. So for the first few years good old FKW/OAG just used to plod between LHR and JFK. And plod she did, superbly. She never did get the ADEUs (not necessary thank goodness when the INUs got modified) but we wired in DME updating and so she could navigate around with the best of them.
My gosh I do prattle on, sorry guys.
Best regards
Dude

PS Welcome back Landlady, hope you've recovered from your fall XXXX
Last edited by M2dude; 15th Jan 2011 at 11:29 .
17th Apr 2011, 10:40
permalink Post: 1300
agreed Dude...
202 was built as 2nd Production, with a defined role as a test aircraft. Several studies were carried out over the years to see if she could be reused. Initially with the manufacturers, where if Concorde has been a success she could have been refurbished and sold to another airline at a "good" price. Of course here flying outside the certified flight envelope led to a lot of further concerns that really was curtains for any modification.
BA had robbed a lot of parts from her in the 80s, especially to bring G-BOAG back into service, so it was a no brainier in the end to put her in a hangar and rob whatever was required to kept the fleet of 7 in the air.
One little point, in the very late 70s here MEPU was decommissioned and she was fitted with the HYRAT...although the guts of the de-contaminated MEPU is still up in her tail cone.
If you want to see an Concorde as it was in Airline Service go visit MAN or EF, fantastic displays showing an Airline Concorde in the 90s or 00s
If you want to visit a Concorde and want to see the 4 stories in one (Concorde story, the unique story of a development aircraft, the airliner passenger experience and they story of how Concorde pilots were trained).... then visit Brooklands.
We've never been able to prove from a documented drawing perspective at Brooklands that the roof of the forward fuselage was any thiner than that of 204.
202 was built as 2nd Production, with a defined role as a test aircraft. Several studies were carried out over the years to see if she could be reused. Initially with the manufacturers, where if Concorde has been a success she could have been refurbished and sold to another airline at a "good" price. Of course here flying outside the certified flight envelope led to a lot of further concerns that really was curtains for any modification.
BA had robbed a lot of parts from her in the 80s, especially to bring G-BOAG back into service, so it was a no brainier in the end to put her in a hangar and rob whatever was required to kept the fleet of 7 in the air.
One little point, in the very late 70s here MEPU was decommissioned and she was fitted with the HYRAT...although the guts of the de-contaminated MEPU is still up in her tail cone.
If you want to see an Concorde as it was in Airline Service go visit MAN or EF, fantastic displays showing an Airline Concorde in the 90s or 00s
If you want to visit a Concorde and want to see the 4 stories in one (Concorde story, the unique story of a development aircraft, the airliner passenger experience and they story of how Concorde pilots were trained).... then visit Brooklands.
We've never been able to prove from a documented drawing perspective at Brooklands that the roof of the forward fuselage was any thiner than that of 204.
