February 02, 2025, 23:05:00 GMT
permalink Post: 11820185
1. In an effort to maximize commercial air traffic in and out of DCA, the FAA has created the “deviate to RWY 33 procedure” for air traffic in-bound to RWY 01. This requires a right-hand turn from the RWY 01 approach followed by an immediate hard left-hand turn to line up on RWY 33. FAA criteria for a stabilized approach states that you have to be stable at 500 feet AGL on final in VMC or perform an immediate go-around. But on this particular approach, you will be at or below 400 feet AGL as you come out of the left turn to final. So the FAA has granted an exception to the “stabilized requirements” at DCA to allow for this maneuver. This allows ATC to shorten the distance between arriving and departing aircraft that are utilizing conflicting RWYs. The FAA in essence violates its own safety standards on stabilized approaches for the sake of expediency.
2. The FAA creates the Route 1/4 helicopter route through the DCA airspace as a VFR route with constantly changing altitude requirements. The lowest limit is at 200 ft MSL through the area east of DCA. Any pilot will tell you that flying that low over water at night is a best a tense experience. Try not to break that limit flying at night while also trying to communicate with ATC and simultaneously searching for possible conflicting aircraft.
3. The United States Army Aviation Branch deems it acceptable to allow training missions for Army Reserve pilots with limited flying experience to fly these helicopter routes through this complex and extremely active airspace. Compounding this, training flights at night using night-vision goggles are deemed “safe” in spite of the fact that using said goggles severely limits peripheral vision and makes it difficult if not impossible to perceive any color other than green and white. Picking out particular lights against the background of urban lighting is challenging, as is depth perception. Scanning key cockpit instruments is also made more difficult, making it challenging to accurately maintain altitude. Add to that workload the need to be in constant communication with ATC as well as monitoring all other comms traffic not directed to you but necessary in order to maintain good situational awareness. Given the density of commercial air traffic on this route, common sense would dictate that this route be flown by only the most experienced pilots and only when absolutely necessary. Reasonable logic would understand that conducting training missions should not be using final approach areas with heavy commercial traffic.
4. The Army crew on PAT25 are flying a mission they have been ordered to fly, at night and using night vision goggles. Although they may feel it is difficult and may be anxious about it, their command structure has determined that it is an appropriate training procedure and as such must meet minimum safety requirements. They do not have the authority to question the mission or the orders to fly it.
5. JIA342 is on approach for RWY 01, but is asked at the last minute by ATC to deviate to RWY 33, requiring the “circle to land” maneuver. Therefore, they are now on approach different from what they briefed for.
6. Any aircraft following the “circle to land” approach to RWY 33 will most likely have both pilots focused on RWY 33 as they come out of the left turn to final, especially if it was a last-minute request by ATC. In this case they will be looking to make sure that AA1630, which has just been given clearance to depart from RWY 01, is clear of the intersection with RWY 33 as they complete their final approach, and be ready for a go-around if it is not. In addition, this left bank makes it extremely difficult for the first officer to see any conflicting traffic coming towards them from the 1 to 2 o’clock position, as that traffic will probably be below the right window level. For the pilot, who is on the left side of the cockpit, visibility of such conflicting traffic will be nearly impossible.
7. For whatever reason, ATC is working with “split frequencies while controlling this airspace, so that although the controller hears both the aircraft on approach and the helo traffic south-bound on “Route 1”, the pilots of those respective aircraft only hear information directed at them. Thus they are not aware of all that is going on around them, and as such their situational awareness is limited by factors outside of their control.
8. ATC informs PAT25 of the conflicting aircraft on approach for RWY 33 at 1200 feet MSL, but at the time, PAT25 is heading almost due east towards the Jefferson Memorial on Helo Route 4 while JIA342 (the CRJ) is executing its right turn departing from the RWY 01 approach and is now heading in a northeast direction as it prepares to make a hard left onto the RWY 33 short final approach. From their respective positions, PAT25 in all likelihood sees the landing lights of AA3130 which is trailing JIA342 and whose landing lights are pointed almost directly in his direction, and mistakenly identifies it as the aircraft approaching RWY 33. At no time does it appear that ATC notifies JIA342 of the conflicting helo traffic. They are most likely focused on their approach to RWY 33, which was just handed to them.
9. As JIA342 rolls out of its left hand turn to final on RWY 33, completing the deviation they were just handed and had not briefed for, it is now approaching the 9-11 o’clock position of PAT25. Since the pilot of PAT25 is on the right-hand side of the Blackhawk, visibility of the CRJ may be limited. Both pilots of PAT25 are now most likely visibly fixated on passing to the rear of AA3130, which is in their 1-3 O’clock position, and which is the conflicting aircraft they perceive as the one ATC initially warned them about.
10. ATC, now receiving a conflicting aircraft warning, asks PAT25 if they have JIA342 in sight. In the absence of any obvious difference from the first mid-identification of the conflicting traffic, confirmation bias raises its ugly head. The voice response from the training pilot is calm and confident in stating that they do have it in sight and claim visual separation, probably proving once again that he mistakenly has AA3130 in sight slightly to his right directly in front of him and more than a mile away. Both pilots are totally unaware of JIA342 which is now arriving in front of them from their left.
11. The collision occurs.
In my humble opinion, the crews of both aircraft involved were set up by both the FAA and the Army Department of Aviation through a series of poorly based decisions which focused on expediency and departed from any appropriate utilization of a rational use of risk assessment. Consider the following:
1. Approval of the circling to RWY 33 maneuver which violates normal stabilized approach standards.
2. The establishment of a series of complex VFR helicopter track complex and heavily restricted air space as well as through final approach paths.
3. A 200 foot maximum altitude requirement over water and required even at night, which may result in a less than 200 foot vertical separation between aircraft on approach to RWY 33 and those traveling on Helo Route 1/4.
4. The decision to conduct military training missions in this complex and busy airspace with an abundance of commercial passenger traffic either arriving to or departing from DCA.
5. The use of split frequencies by the FAA which negatively impacts the situational awareness of all of the pilots in the airspace.
6. The use of night vision goggles to place even more limitations on the pilots.
Granted, all pilots involved may not have had the thousands of hours senior commercial and military pilot possess. But even the most senior individuals when placed in the task saturated environments these two crews faced would have at the very least felt their “pucker factor” increase through this. And there is probably an equal chance that the lack of common sense and appropriate safety design exhibited by the controlling entities would have resulted in a similar outcome. The odds were significantly stacked against these two flight crews, and unfortunately, against the passengers and flight attendants as well. If ever there were an example of an accident waiting to happen, this is it.
Subjects
ATC
Accident Waiting to Happen
Blackhawk (H-60)
CRJ
DCA
FAA
NTSB
PAT25
Route 4
Separation (ALL)
Situational Awareness
VFR
Vertical Separation
Visual Separation
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
February 03, 2025, 15:42:00 GMT
permalink Post: 11820640
(*) I mean control input to maintain visual separation . not last second collision avoidance maneuver.
Subjects
ATC
FAA
ICAO
Radar
Separation (ALL)
VFR
Visual Separation
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
February 03, 2025, 16:32:00 GMT
permalink Post: 11820688
25 ft is the accuracy of mode S, transmit data so let's take 300 ft , Heli was apparently 100 ft higher than its altitude restriction , doing a separation maneuver ? (*) question to my US friends , : when delegating separation VFR to an aircraft does that automatically cancels its previous altitude restrictions ?
(*) I mean control input to maintain visual separation . not last second collision avoidance maneuver.
Subjects
ATC
FAA
ICAO
Radar
Separation (ALL)
VFR
Visual Separation
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
February 03, 2025, 23:26:00 GMT
permalink Post: 11821010
Thanks
Subjects
ATC
Blackhawk (H-60)
IFR
Radar
VFR
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
February 03, 2025, 23:29:00 GMT
permalink Post: 11821012
But for those rebuking any mentioning of a VHF Heli frequency, please provide some proof as any reference I find on VFR sectionals, is a VHF Heli-frequency.
IFR charts only have the regular VHF+UHF TWR freq.
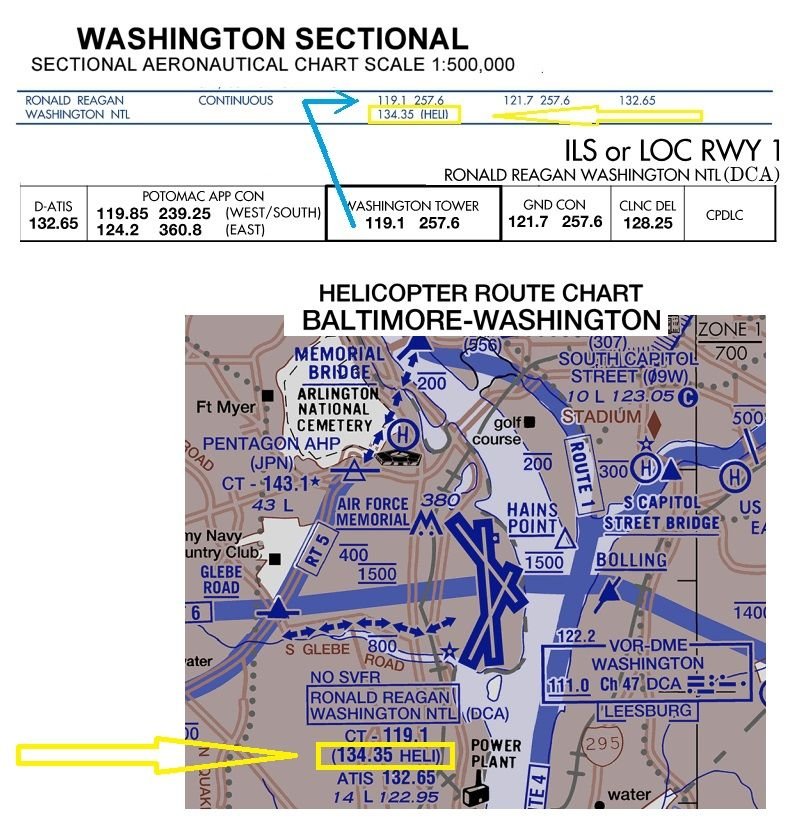
Subjects
IFR
VFR
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
February 05, 2025, 07:14:00 GMT
permalink Post: 11821938
As a previous poster has said, they are using third world procedures at what is a very busy and high-density traffic area. I doubt if this collision would have occurred in many other countries as positive separation and/or significant restrictions are provided to ALL aircraft, be they IFR or VFR, and certainly not at night.
I suspect however that the DoD would not be too happy with not being able to operate VFR. Whatever the outcome, an independent risk analysis would need to tick all the boxes and the procedures changed to match.
Subjects
FAA
IFR
Separation (ALL)
VFR
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
February 05, 2025, 08:11:00 GMT
permalink Post: 11821971
As a previous poster has said, they are using third world procedures at what is a very busy and high-density traffic area. I doubt if this collision would have occurred in many other countries as positive separation and/or significant restrictions are provided to ALL aircraft, be they IFR or VFR, and certainly not at night.
I suspect however that the DoD would not be too happy with not being able to operate VFR. h.
Subjects
FAA
IFR
Separation (ALL)
VFR
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
February 05, 2025, 09:41:00 GMT
permalink Post: 11822038
Additionally, any helicopters flying in such congested airspace should have a display showing other traffic so they know where to look outside.
Subjects
ATC
IFR
Separation (ALL)
VFR
Visual Separation
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
February 05, 2025, 10:12:00 GMT
permalink Post: 11822066
Imho the altitude sectored restrictions were never suitable and safe to deconflict helicopter traffic from traffic to finals 01 and 33, but were meant to deconflict takeoffs from 15 and 19. Could it be that someday some clever soul thought to solve increasing traffic demands by using 33 and 01 for landing despite traffic in the helicopter routes under visual separation rules, ignoring thereby that now all layers of safety had been removed bare the eyes of an helicopter crew?
Subjects
ATC
IFR
Separation (ALL)
VFR
Visual Separation
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
February 05, 2025, 10:32:00 GMT
permalink Post: 11822080
Additionally, any helicopters flying in such congested airspace should have a display showing other traffic so they know where to look outside.
You cannot actively vector a helo at 200ft over the black hole of a river in the middle of an urban environment or anywhere else. You'd kill helos every month doing that. If the helo were at 100ft or so there would be no need for vectors (you never get them in London, just holding, ie orbits if necessary).
Visual acknowlewgement from the aeroplane is totally unnecessary as he is on finals to land which give total priority over all other traffic. It is up to the give-way traffic to identify and acknowlege.
500ft vertical I agree with, in which case 1,5 miles is totally unnecessary and ridiculously excessive.
This discussion is being considerably bogged down by a really surprising (to me) absence of understanding of helos and helo ops by people who clearly only fly f/w IFR and seem to have no concept of how the rest of the aviation world works. Strangely, there are other ways of aviating safely without staring exclusively at an instrument panel, following a magenta line and doing only what someone miles away in an office tells you. You simply cannot try to apply IFR airline type procedures and mindset to low level VFR traffic. It's like a train driver trying to dictate railway rules to a motorcyclist and being unaware that motorcycles just don't operate like trains... imaginingthat helos can or would come to a free air hover for separation is another example of unrealistic imagnation over reality.
Please, if you don't know anything about helicopter ops, please don't try to apply procedural IFR or Hollywood mindsets/misapprehensions to them as if there is no other waay of flying.
Last edited by meleagertoo; 5th February 2025 at 10:54 .
Subjects
ATC
CRJ
Hover
IFR
Separation (ALL)
VFR
Visual Separation
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
February 05, 2025, 10:45:00 GMT
permalink Post: 11822093
Perhaps you mean that DoD would not be too happy with not being able to take visual separation, at night, using NVG? I think they might have to suck that up - especially the second and third aspects.
Subjects
IFR
Night Vision Goggles (NVG)
Separation (ALL)
VFR
Visual Separation
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
February 05, 2025, 11:21:00 GMT
permalink Post: 11822123
Usually, only if crossing LHR you'd be cleared to enter via requested route with limit Bedfont/Sipson, sometimes Airport Spur to hold (orbit) and change from Heathrow Special to Tower for the crossing itself. There's a further hold at Twin Taxiways between the runways. Altitudes are shown. Note there is usually unrestricted passage on routes H3 and H10 along the river directly under the approach. This system works seamlessly and with - to date - total safety.
Accepted the aairport we are discussing has more varied runway directions than Heathrow so the situation would be a bit more complex but I can't see why a similar system couldn't be devised - with defined clearance limits, sensible vertical separation and, critically, coherent and specific controller voice procedure.
There's no reason not to make landing traffic aware of helos holding close in if appropriate and indeed that happens, but no way is their visual contact required.
The entire system operates on visual 'separation'. Helos cross visually behind traffic as cleared, but with vertical separation. It's as safe as the system can be made. How else could it work? It requires no controller vectoring and the time and space margins that would be required if radar separation was used would render the slick, efficient visual system cumbrous, unacceptably high end unnecessary workload and probably unworkable.
Please, once again let's stop applying this insular f/w procedural IFR mindset to VFR helo traffic. There seems to be a procedural IFR mental blockage that can't see that 'visual separation' occurs in three dimensions, not just two. Helos are perfectly capable of ensuring visual separation as long as the traffic has been correctly identified and with vertical separation as here even if a mistake is made there is 800ft clear vertically. Also, VFR does NOT mean, as many seem to imagine, blundering about randomly at will, it is often every bit as disciplined and controlled as IFR as Shackman reiterates below, these routes are rigidly enforced to within a hundred metres or so and woe betide the transgressor.
The elephant in the room here is a combintion of a ridiculously hazardous two-dimensional crossing procedure combined with culpably sloppy & imprecise r/t which offers no second slice of cheese, not matters of visual separation. I'm well aware that our transatlantic cousins are sensitive to criticism of their relaxed, easygoing and informal ways in the air but in this case they self-evidently were the direct cause of 70 odd deaths. While they may regard European style as excessively pedantic there's no doubt whatsoever that had European standards applied here this event would have resulted in nothing more serious than a MOR and an Airmiss report.
For those unfamiliar the light grid squares are 1Km so the Sipson and Bedfont reporting/holding points is ony about 500m from the runways.
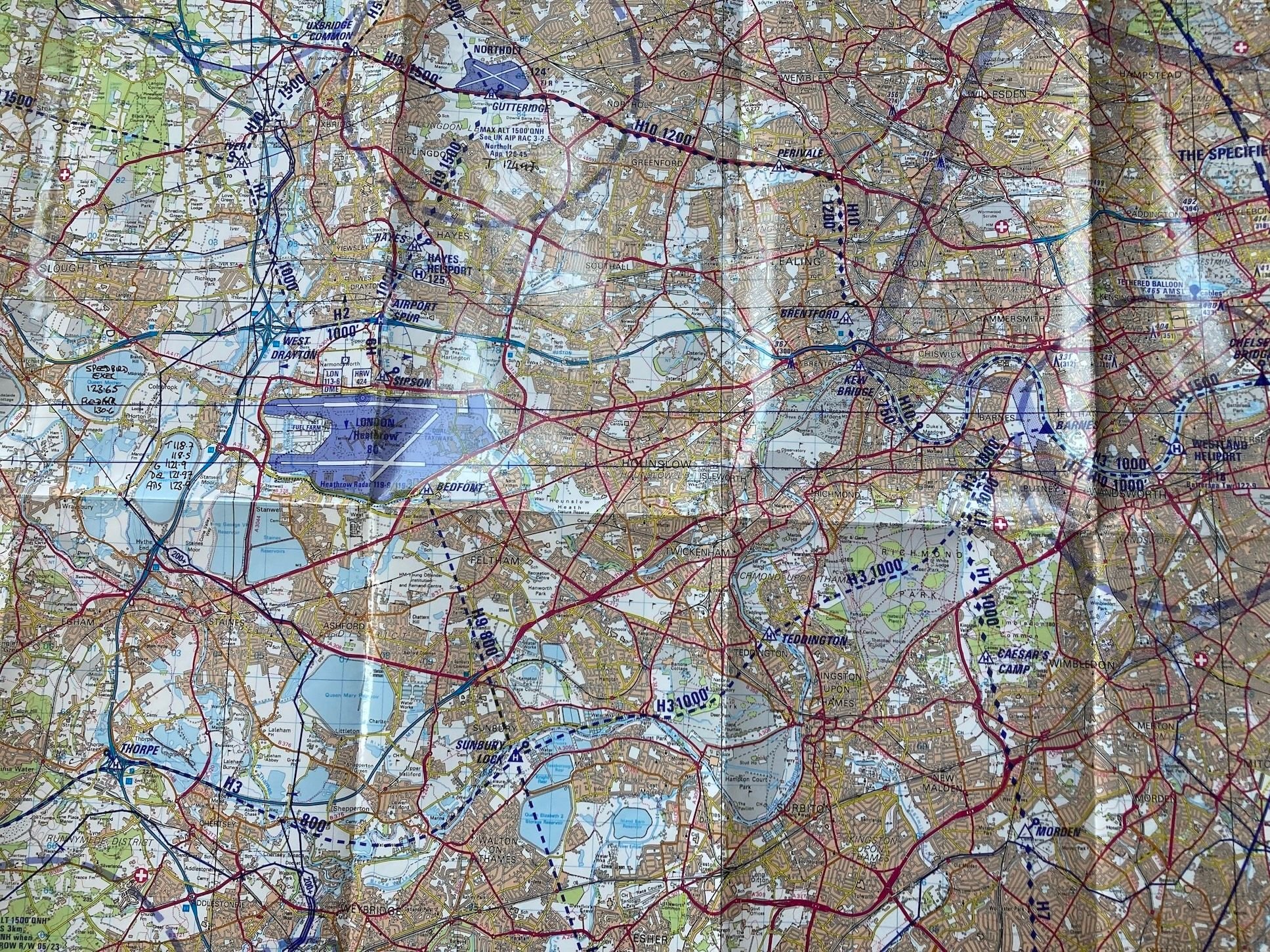
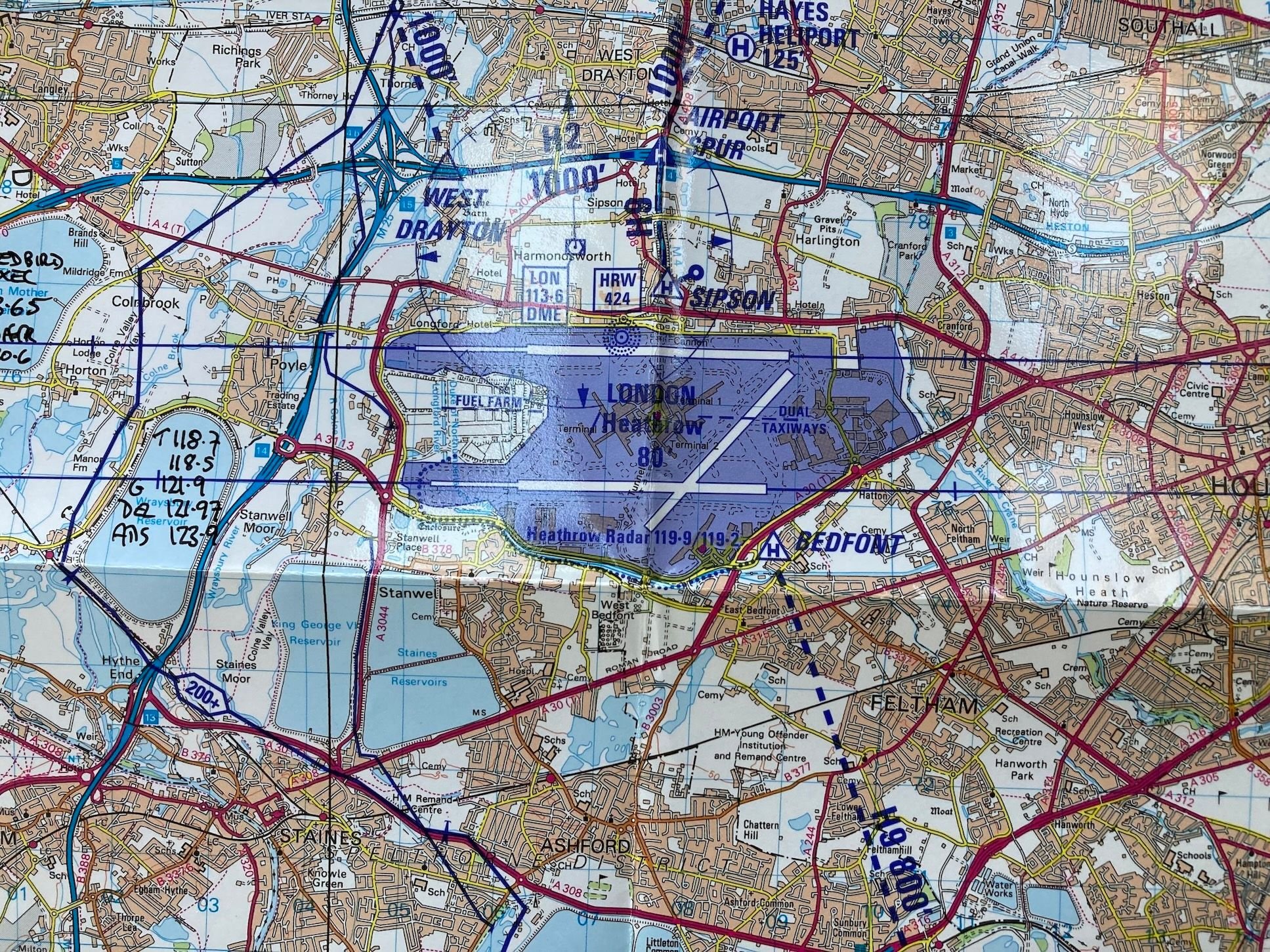

Last edited by meleagertoo; 5th February 2025 at 12:23 .
Subjects
ATC
IFR
Radar
Separation (ALL)
VFR
Vertical Separation
Visual Separation
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
February 05, 2025, 12:57:00 GMT
permalink Post: 11822202
...change from Heathrow Special to Tower for the crossing itself. There's a further hold at Twin Taxiways between the runways. Altitudes are shown. Note there is usually unrestricted passage on routes H3 and H10 along the river directly under the approach...
...defined clearance limits, sensible vertical separation and, critically, coherent and specific controller voice procedure.
I agree with your underlying point that blanket application of IFR separation criteria would be inappropriate. But there are modes of separation besides the false binary of 'visual' and 'IFR' which can be applied to VFR traffic.
Last edited by Easy Street; 5th February 2025 at 14:01 .
Subjects
ATC
IFR
Radar
Separation (ALL)
VFR
Vertical Separation
Visual Separation
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
February 05, 2025, 18:28:00 GMT
permalink Post: 11822429
They were flying Night VFR, not Day VFR.
If I am flying at night over a river at 200' yes, I want to fly smoothly, particularly if my
Maybe, Mech, if you don't know what you are talking about, you keep a sock in it rather than saying something stupid like this:
2. I was sharing (IME means In My Experience) my experience with flying that family of helicopters.
The core problem seems to have been that they never saw the CRJ. Had they seen it, my guess ~ this is speculation ~ is that they'd have turned left and done a 360 degree turn for spacing, particularly since towers instruction was "pass behind" ... and doing that would have, accomplished that. But that isn't how it turned out.
=======
Edited to account for the technical point John Dixson made.
Last edited by Lonewolf_50; 6th February 2025 at 13:10 .
Subjects
CRJ
Pass Behind
Pass Behind (All)
VFR
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
February 06, 2025, 01:45:00 GMT
permalink Post: 11822684
Long answer? No.
Short Answer? "__"
The NW wind results in their CAS being lower if maintaining a desired ground speed, and as LW50 and John Dixson would attest to, the crew would be aiming at generally maintaining speed above ETL, to improve ride and economy, noise, pretty much everything. Civil helos will normally specify a minimum IFR speed to keep tracking tasks of the pilot to a manageable level. The crew in this case are night, VFR, but without SAS or ALTHOLD, helos are a bit more demanding than fixed wing. Flying these helos down in the weeds is why Pilots like Lonewolf and John D got paid the big money and have such extravagant retirement life as of course their Government respects their service that much.

Subjects
IFR
VFR
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
February 06, 2025, 01:54:00 GMT
permalink Post: 11822687
Questions:
Why was PAT 25 search light in the stowed position and not motored to a more forward position?
Why are PAT helicopters not M models with FD's so PAT 25 could have been coupled on route 4 while at 200' giving the PF more time to look for traffic?
Was there pressure to use NVG along route 4 to meet the hourly requirements for currency?
Why did PAT 25 not slow down or hold at Hains in order to pass behind the CRJ as per their clearance?
Why was it ops normal after a near miss the previous day and then only one crew chief instead of two for PAT 25?
Why was the controller task saturated?
Why over the years, as the airport got busier, someone didn't suggest, for night operations, only one aircraft on route 4 or only one aircraft on the approach to 33 at a time and prohibit simultaneous operations?
IMO while the CRJ was turning final to rwy 33 PAT 25 may have experienced the CRJ landing lights in the cockpit and may have chosen up and right rather than left and down. Note worthy, PAT 25 RAD ALT gauge scale changes dramatically at 200'.
Maybe an upgrade to Dulles with a high speed train connection...
Not the latest model? Guess what, combat units get the latest models. These missions are transport, not combat roles. Budgets and priorities rule. There are VH-60s in the battalion, they\x92re probably not scheduled for check rides or training flights.
One RA does not rewrite the schedule, likely not even unusual in DCA. The previous crew may not have passed the event on. I\x92ve had numerous RAs, never a report. The NTSB has stopped asking for reports for events involving VFR traffic.
While nice to have, there\x92s no place for a second crew chief to have a forward view. And the CC may or may not be \x93in the loop\x94. They\x92re crew chiefs, not pilots. We had them on C-5 and they mostly slept in flight as they too much to do on the ground.
Subjects
ATC
CRJ
Close Calls
DCA
NTSB
Night Vision Goggles (NVG)
Pass Behind
Pass Behind (All)
Route 4
TCAS RA
VFR
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
February 06, 2025, 03:31:00 GMT
permalink Post: 11822714
How can you make that statement without realising how many red flags are in it?
LD
Subjects
DCA
NTSB
TCAS RA
VFR
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
February 06, 2025, 11:55:00 GMT
permalink Post: 11822926
PAT25: "PAT25 has the traffic in sight, request visual separation"
Tower: "Visual separation approved"
0:26 here:
https://youtu.be/r90Xw3tQC0I?feature=shared
Perhaps, and this is big perhaps, it's a pavlovian response to whenever PAT is advised of other traffic. I listened to the TCAS RA missed approach from the previous day, and once again the response from PAT is "request visual separation". It's highly likely that the pilot requests for visual separation is the only way that this Class B airspace can operate with the mix of IFR vs VFR, and aerodrome traffic vs transits.
I fail to understand why PAT is using UHF, surely this is another slice of cheese.
The use of RWY 33 for arrival makes it easier for the ATC and the aircrew with one less runway crossing after they have landed. To emphasis the point, the following PSA actually requests RWY 33.
Subjects
ATC
CRJ
IFR
PAT25
Separation (ALL)
TCAS (All)
TCAS RA
Traffic in Sight
VFR
Visual Separation
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
February 07, 2025, 00:03:00 GMT
permalink Post: 11823326
I wouldn't be surprised it's a high percentage of the Heli route1 & 4 traffic that requests "Visual Separation".
Have been listening to a few of LiveATC recordings. On the recording combining TWR & Heli frequencies, you can hear all transmissions (which sometimes overlap), however overall quality is poor. Nevertheless, I get the impression "request Visual Separation" is a common thing.
On the recording of the TWR VHF-frequency only, quality is good, but you don't get the requests/replies from the Heli's, so it's not always clear what was being requested/approved.
Subjects
Separation (ALL)
VFR
Visual Separation
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
February 07, 2025, 00:09:00 GMT
permalink Post: 11823328
Did the FAA or the Army assume they would always be able to apply visual (NOT VFR) separation. Visual separation does not necessarily mean 500\x92 vertically and 1.5 nm or radar target separation; it means \x93I see you, I miss you\x94. Did the operating plan always direct crews to use visual separation as the default plan? I hope not, but it is only I see it being written.
Subjects
FAA
IFR
Radar
Route 4
Separation (ALL)
VFR
Visual Separation
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.