September 07, 2010, 12:45:00 GMT
permalink Post: 5919443
 .
.
As we're on landing gear.
Why was the sidestay a telescopic affair? Most aircraft use a hinged geometric lock arrangement. More weight saving or down to available space in the landing gear bay?
Subjects
Airbus
Landing Gear
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
September 07, 2010, 13:07:00 GMT
permalink Post: 5919495
 .
.
Dude

Subjects
Airbus
Landing Gear
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
September 07, 2010, 14:07:00 GMT
permalink Post: 5919617
In fact quite a bit was transferred from previous aircraft designs to Concorde , such as the 4 fwd cabin door are very similar to that of the VC-10 as is the oxygen system.
Subjects
Landing Gear
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
September 08, 2010, 09:20:00 GMT
permalink Post: 5921203
For some reason I thought that BA used Dunlop and AF Michelin.
EXWOKS explanation of the mechanics of why the Concorde tyre had such an incredibly stressful and vulnerable life, as well as the design makeup of the NZG tyre is as usual 100% correct; a high speed, very high pressure tyre bearing virtually the entire weight of the aircraft right up to the point of rotation.
EXWOK
Dude

Subjects
Air France
Air France 4590
British Airways
Landing Gear
Tyres
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
September 08, 2010, 17:40:00 GMT
permalink Post: 5922316
Regards
Nick
Subjects
Landing Gear
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
September 09, 2010, 00:09:00 GMT
permalink Post: 5923119
 A small handpump is used to ensure downlock after freefall extension. (The Dash 8 and Fokker 50 have - much larger and draggier - backwards retracting main gear, assisted by handpump and springloading respectively for downlock after emergency freefall extension.)
A small handpump is used to ensure downlock after freefall extension. (The Dash 8 and Fokker 50 have - much larger and draggier - backwards retracting main gear, assisted by handpump and springloading respectively for downlock after emergency freefall extension.)
Thanks to all Concorde experts for this truly wonderful thread. The ingenuity of design and the complexity of design that enabled the technological marvel that is Concorde never cease to amaze this humble airline driver. Having missed the opportunity to fly on Concorde is high on my list of aviatic regrets as well, and I'll have to make do with the memories of watching Air France Concordes taking off from CDG during our turnarounds there.
I could (and actually have) spent hours following this thread.
Is it true that Concorde was always flown by the highest seniority BA captains, copilots and flight engineers? Would Concorde usually be the last rung on the ladder before retirement for Captains/FEs or was it usual to return to slower equipment after a stint on Concorde?
And, sorry if I missed this, would Concorde thrust levers move during autothrottle operation?
Lastly, Concorde was originally to have had a large moving map system. Any insights into why and how that got scrapped along the way?
Thanks!
Subjects
Auto-throttle
British Airways
CDG
Captains
Landing Gear
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
September 09, 2010, 11:58:00 GMT
permalink Post: 5924008

Subjects
Landing Gear
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
September 09, 2010, 12:44:00 GMT
permalink Post: 5924106
Concorde was without doubt the first ever aircraft to have a fully automatic, active braking system, with NO mechanical linkages to the brakes whatsoever: Firstly there was the 'normal' anti-skid, but the Concorde system was far from normal. Instead of the universally used anti-skid concept that monitors main wheel deceleration, we of course did it differently. Main wheel rotational velocity was compared with (un-braked of course) nose wheel rotational velocity. With zero skid the RELATIVE velocities would of course be the same, any difference would relate to the % skid value. That was the the real advantage of 'our' system; the percentage of main wheel skid could be calculated by the SNECMA (Hispano) SPAD Box, maximum runway 'stopping power' being achieved at around 20% skid. (I always thought that it was strange, the maximum runway adhesion being achieved while the wheel was skidding, but that's what it said on the tin). When the aircraft initially touched down, and the braking/anti-skid system was enabled, a fixed nose wheel speed Vo was used until the nose wheel touched down. (Can't quite remember what equivilant ground speed this related to though).
As well as anti-skid there was also torque modulation also, due to the use of carbon fibre brakes and the enormous amount of rotational torque involved. (A maximum figure of 8.5 MILLION ft./lbs. of torque springs to mind!!!). When a brake demand was input into the BRAKE ADAPTOR BOX (this also manufactured by SNECMA /Hispano) it was compared with a reference torque. As this brake demand input was applied to the 'box', the torque feedback from a torque link connected at one end to the brake would feedback the actual applied torque, where it was compared to reference torque, and the demand was modulated to suit.
The beauty of it all was that the anti-skid, basic brake demand as well as brake torque limits could all be superimposed on one another, giving a wonderfully flexible system that the pilots could have and did had an enormous amount of faith in.
Dude

Subjects
Anti-skid
Braking
Landing Gear
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
September 09, 2010, 16:06:00 GMT
permalink Post: 5924548
Anyone who travelled in the beast will know that we didn't use the brakes gently - they worked far better if you stood on them firmly and also seemed to wear less; certainly there seemed to be a lot more dust on the wheels if you used them gently.
Taxying out one had to be careful, it was easy to get a brake temp light on (was it 200degs? 220?) which meant waiting ages for it to cool. The watchword was minimum number of brake applications and make them firm, not feathery. And be careful on the lightweight departures as you needed them more.
Subjects
Braking
Landing Gear
V1
V2
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
September 09, 2010, 16:44:00 GMT
permalink Post: 5924634
Mate I know the Concorde V Speeds, my query relates to the comparison with the 744.

Regards as ever EXWOK
Dude

Last edited by M2dude; 9th September 2010 at 22:47 .
Subjects
Anti-skid
Braking
Landing Gear
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
September 11, 2010, 10:43:00 GMT
permalink Post: 5928163
Can any of the learned design types on this forum tell about the considerations involved - was there a procedure to handle it, or would it just do a pole vault and compress into an accordion? Were special design features incorporated to make such an event unlikely, or was it even survivable?
Subjects
Landing Gear
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
September 11, 2010, 11:41:00 GMT
permalink Post: 5928251
Being rearward lowering, the airstream of course helps matters a lot with respect to the nose leg lowering
One of the wing'd chappies I'm sure can come up with the flight procedure for such an event. (Never happened in the 35 years of Concorde flight testing and airline operation).
Dude

Subjects
Landing Gear
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
September 11, 2010, 15:59:00 GMT
permalink Post: 5928677
It's a halfway interesting "what if" question...
Bearing in mind the c.g. is already almost over the main wheels... could it have been done by moving the c.g. as far back as possible, keeping the droop nose at 0\xb0, and after touchdown keeping the nose off the ground for as long as possible?
The radome would have shattered, but the droop nose structure would have acted like a skid.
Just as well nobody ever needed to try it.
There is only one well-known case of a landing gear problem.
Visualise a moment the main landing gear. The main leg 'l' is held down in the vertical position by a large hydraulic "stay" '\' .
___
\l
(I know that, to most people, it looks at first like the retraction cylinder, but it isn't. The retraction cylinder is much shorter, and inside the wheel bay.)
Now the story... It happened during what was going to be the last-but-one flight of the British prototype, 002, during a demonstration flight at Weston-super-Mare.
After a slow pass with the gear down, the co-pilot flying the aircraft put it into a steep turn, retracting the gear at the same time.
The next moment, there was a very loud bang, and one of the main gear lights did not go "green".
Somebody from the crew went to the back cabin, where there is a small porthole to look into the wheel well. When asked what he could see, the answer was "nothing..." ; both the main stay and the retraction cylinder had parted company with the aircraft, and the gear leg was dangling free.
The pilot, John Cochrane, took over the controls, and brought the aircraft back to Fairford. With his guardian angel doing overtime, he managed to put down the aircraft and keep it straight during the roll-out, without the gear collapsing.
I didn't see the landing, but I saw 002 in the hangar the next day. By that time a steel bar had been fitted to keep the leg upright, but the damage was still impressive.
Later on, a spare stay was fitted, but 002s flight test career was over. She stayed in storage at Fairford for some time, and was then flown to the Fleet Air Arm Museum in Yeovilton, where she still can be seen to this day.
Wisely, for the few minutes flight, they did not retract the gear....
CJ
Subjects
Fairford
Hydraulic
John Cochrane
Landing Gear
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
September 11, 2010, 21:39:00 GMT
permalink Post: 5929158
Since you were discussing the scenario of a nosewheel not lowering and that the CG was over the main wheels may I suggest a rather (amusing at least)
possibility ?!!
With a nose gear jammed up but all other gear lowered normally could the Flight Engineer pump fuel rearward adjusting the CG aft sufficiently to allow the Concorde to settle back on her 'Tailwheel'
I realise there would be some damage, especially in light of what has been said about the occasional tailwheel contacts but I imagine it would be less than lowering the unprotected forward fuselage onto the runway.
Of course some pax might have to move to the back of the cabin too !
If the CG was adjusted this far aft would there be controllability issues ?
There could finally be a use for the 'full down position of the visor' landing in this attitude !
Subjects
C of G
Landing Gear
Tailwheel
Visor
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
September 11, 2010, 22:24:00 GMT
permalink Post: 5929197
Let's admit that being faced with that nasty situation in reality would not have been amusing....
But kicking the idea around a moment, why not? It's what I did seeing the question at first.
I realise there would be some damage, especially in light of what has been said about the occasional tailwheel contacts but I imagine it would be less than lowering the unprotected forward fuselage onto the runway.

One thing that promptly occurred to me for this 'no nose wheel' scenario is braking, since both engine reverse and main gear wheel braking act below the CG, so they'd both act to pull the nose down.
At some point, stick fully back, hence elevons fully up, will no longer be enough to fully counteract that, so you'll have to cancel reverse and braking, and probably commit to an overrun.
Your scenario of doing it as a 'three-pointer' on the tail might wel be the better one !
And while we're at it, what about ditching a Concorde?
It's hinted at in the Safety Cards.
It's been tried lots of times, with models in water tanks.
It wasn't really feasible.......
CJ
Subjects
Braking
C of G
Elevons
Landing Gear
Tailwheel
Visor
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
September 12, 2010, 11:10:00 GMT
permalink Post: 5929870
Now you really have upset my Sunday as after many years being retired I have had to go up to my attic to get the Concorde books out so as to answer your question

Anyway as M2dude has said there were drills for everything on Concorde and if I remeber correctly the figure came to 194 seperate drills with 13 of them having a memory content. Never mind remembering the memory content it was hard enough sometimes to remember which drill had a memory content
Anyway I have found the drill for
"Landing with Nose gear not locked down "
To give just the essence of the drill you are asked to
Jettison as much fuel as possible
Set the C of G for landing to 53%--- sitting over main gear
After gear lowered select Standby lever to down position----- This ensures the gear jacks remain pressurized down on touch down
After lowering nose/visor on normal system seltct visor stby system to visor down---- this removes hyds from nose and visor system down jacks, so allowing nose/visor to raise if nose leg collapses
Brake lever to standby --- If nose leg collapse there is no ref anti skid signal and normal brakes would not work. Standby has no anti skid system and will work
Then on landing nose up attitude should be maintained and normal engine reverse selected as soon as possible remembering that engine reverse tries to pitch the aircraft nose up
Wheel brakes use gently and cease at 120kts
At 110 kts reduce attitude to touch nose wheel down gently
At 85 kts select engine reverse to idle power
At rest " Passenger Evacuation"
----------------------------------------------
So you can see this drill uses the nose up effect of engine revese to hold the nose gear off the ground for as long as possible.
I fear this explanation will gemerate more questios than it has answered, but
off for a cup of coffee now as grey cell are hurting

Last edited by Brit312; 12th September 2010 at 11:34 .
Subjects
Braking
Landing Gear
Visor
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
September 13, 2010, 14:54:00 GMT
permalink Post: 5932115
In May 1977, aircraft G-BOAA was returned to Filton for some modifications that .....
In "Concorde - The Inside Story" by Brian Trubshaw there is actually a photo of what is almost certainly the same incident.
But there is another story....
After the first-ever landing at Bahrain, a crowd of Very Important Persons was allowed to visit the aircraft.
Of course they had to see it all, including the rear cabin.
Since the aircraft hadn't been refuelled yet, the inevitable happened... the aircraft started slowly but inexorably tilting backwards.
A very undignified stampede towards the front resulted, just in time, so the aircraft did not actually sit on its tail.
But there was a sequel. The incident had been watched by the airport manager, who promptly decreed that from then on a tractor would have to be chained to the nose gear whenever the aircraft was on the ramp.
Urban legend has it, that from then on there was a new item in the pre-taxy checklist for Bahrain.
CHAIN REMOVED FROM NOSEWHEEL - CHECK
CJ
Subjects
Air France 4590
Brian Trubshaw
Checklists
Filton
G-BOAA
Landing Gear
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
September 28, 2010, 22:58:00 GMT
permalink Post: 5962512
Nevertheless there were three separate sets of landing/taxi lights there.
Quoting from the manual:
Two main landing lamps, one mounted in each wing root leading
edge, have retractable/extensible mountings and when not in
use are retracted in the lamp housing.
Two land/taxi lamps, similar to the main landing lamps, are attached to the
nose landing gear bay doors. The land/taxi lamps extend to
an intermediate position for landing, upon which they
automatically extend to the full position for taxiing, thus
changing the beam angle to compensate for the attitude change.
Two taxi/turn-off lamps, one mounted on each side of the
forward fuselage, provide ground illumination to identify
runway turn-off points.
These are the 'main' lights in the wing leading edge (600W each).
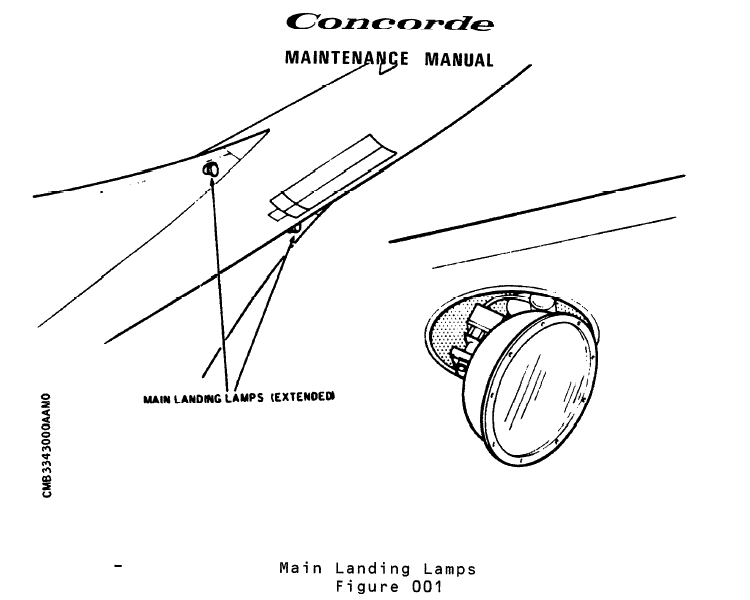
These are the lights in the nosewheel doors ("only" 450W each).

The heat was less of a problem, actually.
The lights themselves were high-power sealed-beam units, the main units were 6 00W each, and the ones in the nosewheel doors were 450W ... nothing like your car headlights.
As a matter of fact, on the ground you were not suppossed to turn them on any more than 5 minutes in any 10 minutes.... they got a lot hotter when switched on, than they did in supersonic flight.
What happened was that the main landing lamps in the wing roots were angled such, that they pointed straight ahead at the right angle to "hit" the runway during the landing itself.
Once the aircraft touched down, the land/taxi lights in the nose gear door extended further and lit a wider expanse of the runway ahead (see the earlier quote from the manual).
And then the third set of lights in the nose helped you to find the turn-off to the taxiway.
One nice little detail.... on F-BTSD, the Concorde at the French Le Bourget museum, those lights still work, and on G-BBDG, the Concorde at the Brooklands museum that was saved from the scrapheap, they brought those lights back to life, too.
CJ
Last edited by ChristiaanJ; 28th September 2010 at 23:14 . Reason: Addng pics and typo
Subjects
Brooklands
F-BTSD
G-BBDG
Landing & Taxy Lights
Landing Gear
Le Bourget
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
September 29, 2010, 14:38:00 GMT
permalink Post: 5963836
Judging by the picture from the maintenance manual below, once the nosewheel was down, the main landing lights just lit up the ground below the nose, but not ahead.
Did you just rely on the runway lighting plus the ambient light (town lights reflected by the clouds, etc.) or did you usually extend the nosewheel door lights once you were down?
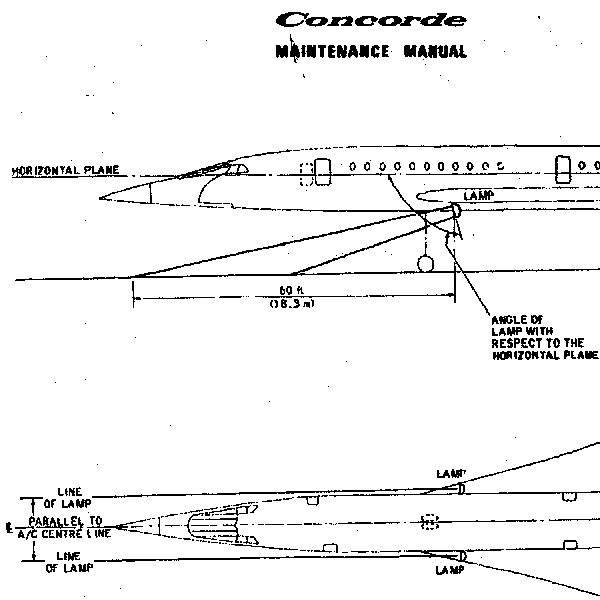
CJ
Subjects
Landing & Taxy Lights
Landing Gear
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.
October 08, 2010, 13:26:00 GMT
permalink Post: 5981897

In early 1977, aircraft 210, G-BOAE was doing it's pre-delivery test flying out of Filton (Fairford was now closed as a permanent test base, but day flying was carried out from there, the aircraft returning to Filton at night). and it was decided to try this rechnique on 210. A little French guy from the landing gear manufacturer Messier spent all day, travelling from the other side of France to Filton in the west of England, and arrived at the plant at around 23:30. He spent several hours that night, draining off his carefully calculated amount of fluid from each of the main landing gears, and returned to France a happy little bunny the following morning. BIG MISTAKE !!

When OAE did it's test flying the following day, everything seemed to be going well, but on the final landing of the at Fairford.. THUMP!!! The barrels of the shock absorbers bottomed, sending a sizable shock through the entire airframe. No structural damage was done, but several systems went off line, and I particularly remember one of the incidence vane heaters being knackered by the force of the vane thumping against the stops. Our poor little Messier rep' arrives home LATE that night, only to receive a message telling him to go straight back to Filton. The poor guy was a wreck, but like a true trooper headed straight back to the UK, and inserted his carefully measured amount of oil back into the main landing gears of G-BOAE. (Always thought that this would have made a great comedy sketch)

Dude

Subjects
Fairford
Filton
G-BOAE
JFK
Landing Gear
Links are to this post in the relevant subject page so that this post can be seen in context.
Reply to this quoting this original post. You need to be logged in. Not available on closed threads.